Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
L
e
3
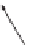
Figure 10.15 A thrown plate describes a parabolic path while wobbling. The small circle
indicates the position of a mark on the rim of the plate. The direction of the
e
3
axis is
indicated. The underside of the plate is shaded and each image represents the orientation of
the plate at successive time intervals of
π/(
2
ω
p
). Note that when the
e
3
axis has precessed
by 2
π
radians the mark has rotated by
π
radians.
We are finally at the point where we can give a complete description of the
combined rotational and translational motion of a plate in flight
7
. Suppose that the
plate is thrown like a Frisbee, then
L
will be approximately vertical as shown in
Figure 10.15. The centre of mass of the plate will obey Newton's Second Law
(Eq. (2.28)) and so will follow a parabolic path typical of motion of a particle in
a uniform gravitational field. The wobbling motion that we have described in this
section then takes place in a frame of reference with its origin at the position of
the centre of mass. This separation of the motion into that
of
the centre of mass,
and rotation
about
the centre of mass is valid even though the centre of mass is
uniformly accelerating, as we discussed in relation to the derivation of Eq. (4.13).
10.6.3 The wobbling Earth
Does the Earth wobble as it travels spinning through space? Provided that we
ignore the variation in the gravitational field of the Sun and Moon over the volume
of the Earth, then there is no gravitational torque and we might well consider the
Earth to be a free symmetric top. The shape of the Earth is oblate (squashed at the
poles) so that
I
3
is a little larger than
I
. The numerical values are such that
I
3
−
I
≈
0
.
0033
,
I
ω
which we can substitute into Eq. (10.59) to obtain the precession frequency of
about
e
3
in the body-fixed frame of an Earth-bound observer:
I
3
−
I
10
−
3
=
ω
t
=
3
.
3
×
×
2
π/
day
.
(10.84)
I
This gives a period of about 300 days. We therefore expect that the axis of rotation
of the Earth, as observed from a frame of reference fixed to the Earth, should
precess about the North Pole with a period of about 10 months. This motion
7
We ignore air resistance.