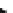Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Baseline
underlying surface
Simulation results with
baseline underlying surface
AVHRR data, 1993
Atmospheric forcing
data of RCP 6.0from
CMIP 5
WRF-ARW
model
Effects of future urban
expansion on climate
Land use and cover
data of RCP 6.0,
2010-2100
Predicted
underlying surface
Simulation results with
predicted underlying surface
Fig. 7.23
Simulation scheme and data processing framework
7.5.1.2 Data and Process
An AVHRR grid data of 1 km 9 1 km of the United States Geological Survey's
(USGS) classification system spanning a 12 month period (April 1992-
March1993, henceforth, 1993) is used as the baseline underlying surface data in
this study (Fig.
7.21
). And the predicted land use and land cover data of
0.5 9 0.5 from 2010 to 2100 are derived from the Asia-Pacific Integrated Model
(AIM) modeling team at the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES),
Japan. The reason that we choose RCP 6.0 is because it is a stabilization scenario
where total radiative forcing is stabilized after 2100 without overshoot by
employment of a range of technologies and strategies for reducing greenhouse gas
emissions (Y. Hijioka
2008
). Supposing other type of land use and cover
remaining stable, the new urban area pixels derived from the AIM output of RCP
6.0 were overlaid to the map of baseline underlying surface. Consequently, two
major underlying surface data, including the baseline underlying surface data
directly derived from AVHRR data of 1993 and the predicted underlying surface
data by overlaying the urban expansion information to the map of baseline
underlying surface, were finally obtained (Fig.
7.23
). Both of these two underlying
surface data were transformed into grid data with a 50 km 9 50 km resolution by
resampling (Fig.
7.24
). According to the AIM data, urban area in the Northeast
megalopolis had expanded rapidly during the period 1993-2010 and would con-
tinue to expand during the period 2010-2100. Model output, such as air temper-
ature, specific humidity, sea level pressure, eastward wind, northward wind, and
geopotential height from 2010 to 2100 were used as the atmospheric forcing
dataset of WRF-ARW model (Fig.
7.23
).
7.5.1.3 Simulation Scheme
The WRF-ARW model based on the Eulerian mass solver is used in this study to
investigate the temperature and precipitation change driven by future urban
expansion in the study area. Simulation from 2010 to 2100 with a constant