Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
Urban and built-up land
Dryland, cropland, and pasture
Irrigated cropland and pasture
Cropland/grassland mosaic
Cropland/woodland mosaic
Grassland
Shrubland
Savanna
Deciduous
broadleaf forest
Water bodies
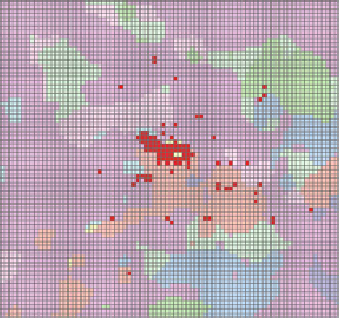
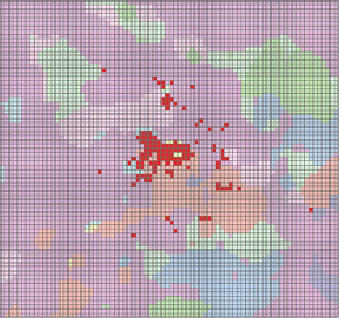
Fig. 6.18 Underlying surface data of Wuhan Metropolitan under different scenarios. a Baseline
scenario. b Centralized urbanization scenario. c Decentralized urbanization scenario
effect difference of three scenarios appears at the hottest month of the year (June,
July, and August). In colder months (January, February, November, and December),
the difference of warming effect under three scenarios is small.
Under different scenarios of urbanization, there are significant differences of
spatial patterns of impacts of land surface on temperature change (Fig.
6.20
). From
the differences of three scenarios, variation between centralized and decentralized
urban land expansion scenario is the biggest, while there are small differences
between centralized urban land expansion scenario and baseline scenario. Com-
pared to decentralized urban land expansion scenario, the spatial range of warming
effect is much stronger under centralized urban land expansion scenario, and the
magnitude of temperature difference was greater too. Compared to baseline sce-
nario, the spatial range of warming effect was a little stronger and more concen-
trated
in
centralized
urban
land
expansion
scenario,
and
the
magnitude
of