Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
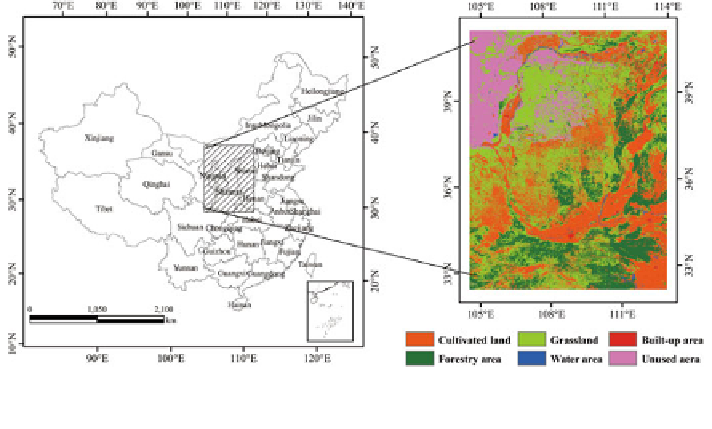
Fig. 5.9 Location of the study area and the distribution of land use type in the overgrazing areas
of Northwest China
while this study aims to explore the potential impacts of grassland degradation on
climate change in overgrazing area of Northwest China from 2010 to 2040.
5.3.1 Data and Methodology
5.3.1.1 Case Study Area
The overgrazing area of Northwest China is located between 104 04
0
and
114 02
0
E, 3240
0
and 41 20
0
N, with a total land area of 811,856 km
2
, and
covers five provinces including Ningxia Province, the southeast part of Gansu
Province, Shaanxi Province, the western part of Shanxi Province, and the middle
and southwest part of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (Fig.
5.9
). This area
stretches across the eastern monsoon region and northwest arid region, with an
annual average temperature of 5-10 and the annual precipitation of 200-800 mm,
and is close to the Qinghai-Tibet alpine region, approximately located in the
transition zone of the three major natural zones of China. There is very limited
water resource, the spatiotemporal distribution of which is very imbalanced, and
there are frequently meteorological disasters. It is one of the largest grazing areas,
and is also the major production base of the animal husbandry industry in China.
The grassland and cultivated land are the dominant land use types in this region,
accounting for 36.19 and 29 % of the total area, respectively. The irrational uti-
lization of grassland resources is very common due to overgrazing and over-
reclamation under the background of one-sided pursuit of economic benefit since
the 1980s, which has led to the continual degradation of the grassland. The