Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
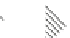
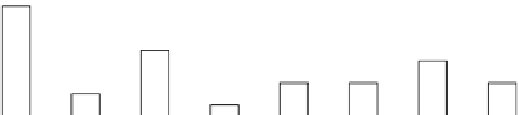
0.12
Temperature change
/year
0.1
0.08
0.06
0.04
0.02
0
dryland
cropland
and
pasture
irrigated
cropland
and
pasture
deciduou
s
broadleaf
forest
barren or
sparsely
vegetated
land
urban
and built-
up land
water
bodies
grassland
wetland
Temperature change
0.1
0.02
0.06
0.01
0.03
0.03
0.05
0.03
Fig. 4.16
Temperature change in various land use/cover types
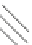
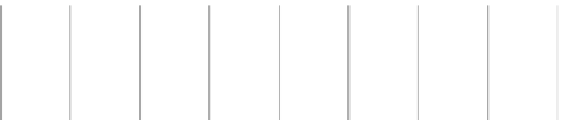
0.15
Temperature change
/year
0.1
0.05
0
-0.05
-0.1
-0.15
Conversi
on from
dryland
cropland
to
grassland
Conversi
on from
grassland
to
dryland
cropland
Conversi
on from
dryland
cropland
to built-
up land
Conversi
on from
dryland
cropland
to water
bodies
Conversi
on from
forest to
dryland
cropland
Conversi
on from
dryland
cropland
to forest
Conversi
on from
forest to
grassland
Conversi
on from
grassland
to forest
Temperature change
0.01
0.02
-0.1
0.04
0.04
0.13
0.12
0.04
Fig. 4.17
Change of the near-surface temperature corresponding to each kind of land use/cover
change
increase the net radiation of land surface, and consequently make the sensible heat
increase and lead to the increase of the daily average temperature.
4.3.3 Concluding Remarks on the Studies of North China
The land use/cover change in the North China Plain during 1992-2005 is mainly
characterized by the increase of urban and built-up lands and the decrease of
dryland croplands. The urban and built-up lands increased by 2.12 %, and the
dryland cropland decreased by 1.59 %, while other land use/cover types changed
by no more than 0.5 %. Besides, the newly increased urban and built-up land is
mainly located in the Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan zone and around large and med-
ium-sized cities such as Shijiazhuang, Zhengzhou, Ji'nan, Qingdao, and Lian-
yungang. In addition, the newly increased
urban and built-up lands mainly