Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
In addition to using ATP to store energy, the cell stores and releases hydrogen atoms from
biological oxidation
e
reduction reactions by using nucleotide derivatives. The two most
common carriers of reducing power are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotin-
amide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP).
O
O
O
NH
2
HO
O
P
O
+
N
5
NH
2
O
HO
P
O
O
4
1
+
N
5
2
3
O
HO
P
O
O
4
1
HO
OH
NH
2
3
2
N
O
HO
P
O
HO
OH
N
5
NH
2
O
N
N
N
O
4
1
3
2
N
5
O
N
HO
N
O
4
1
3
2
HO
OH
P
HO
OH
O
(NADP)
(NAD)
In addition to this important role in cellular energetics, the nucleotides are important
monomers. Polynucleotides (DNA and RNA) are formed by the condensation of nucleotides.
Nucleotides are linked together between the 3 and 5 carbons' successive sugar rings by phos-
phodiester bonds. The structures of DNA and RNA are illustrated in
Fig. 2.31
.
DNA is a very large threadlike macromolecule (MWof 2
10
9
Da in E. coli) and has the
three-dimensional structure of a double-helix. The sequence of bases (purines and pyrim-
idines) in DNA carries genetic information, whereas sugar and phosphate groups perform
astructuralrole.ThebasesequenceofDNAiswritteninthe5
3 direction (starting at
the 5th carbon in one sugar unit and moving toward the 3rd carbon in another sugar unit
as shown in
Fig. 2.30
), e.g. pAGCT (p represents the terminal phosphate group, situated
before the 3rd carbon of the new sugar unit). The double-helical structure of DNA is
depicted in
Fig. 2.32
. In this structure, two helical polynucleotide chains (strands) are
coiled around a common axis to form a double-helical DNA, and the chains run in oppo-
site directions, 5
/
/
3and3
)
5. The main features of the double-helical DNA structure
are as follows:
(1)
The phosphate and deoxyribose units are on the outer surface, but the bases point toward
the chain center. The planes of the bases are perpendicular to the helix axis.
(2)
The diameter of the helix is 2 nm. The helical structure repeats after ten residues on each
chain, at intervals of 3.4 nm.


































































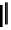






Search WWH ::

Custom Search