Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
OH
O
O
O
OH
O
O
OH
-O-4
-O-4
-1
OH
OH
O
O
O
O
OH
OH
O
O
OH
-5
-
5-5
OH
O
O
O
OH
O
O
O
O
O
OH
O
-O-
4-O-5
dibenzodioxocin
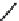
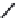
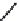
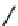
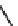
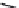
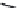
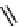
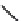
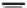
FIGURE 2.28
Common linkages between phenylpropane units in lignin.
2.3.5. Lipids, Fats, and Steroids
Lipids are hydrophobic biological compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in
nonpolar solvents such as benzene, chloroform, and ether. They are usually present in
nonaqueous biological phases, such as plasma membranes. Fats are lipids that can serve
as biological fuel-storage molecules. Lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides are other
types of lipids, which appear in the biological membranes of cells. Cells can alter the
composition of lipids in their membranes to compensate (at least partially) for changes
in temperature or to increase their tolerance to the presence of chemical agents such as
ethanol.
The major component in most lipids is fatty acids. A list of common fatty acids is pre-
sented in
Tabl e 2 .6
. The hydrocarbon chain of a fatty acid is hydrophobic (water insoluble),
but the carboxyl group is hydrophilic (water soluble). A typical fatty acid can be repre-
sented as
CH
3
ð
CH
2
Þ
n
COOH

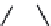

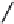
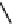









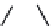

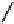
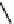





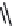



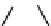

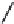

















































































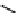
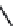












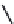

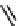










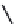

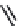






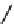






















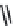
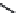

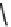


















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search