Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Unselectable mutations
do not provide a survival advantage to the bearer individuals.
Selecting individuals (or organisms) with a desirable but unselectable mutation from the
wild type is extremely difficult and requires special techniques. Even with mutagens,
the frequency of mutation is sufficiently low to prohibit a brute force screening effort for
most unselectable mutants.
1.
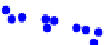
One technique to isolate, for example, cells that cannot synthesize the amino acid
histidine is called replica plating. Cells or microbes are cultured on complete media
to form distinct colonies; then, a replica of this master is made on (1) a complete
medium, and (2) on a minimal medium lacking histidine. The colonies that do not grow
on the minimal medium but grow on the complete medium are the ones that cannot
synthesize histidine, as illustrated in
Fig. 14.2
.
2.
Recombinant technology with replica plating
d
in this method, a population of cells are
infected with a desired unselectable gene segment combined with a vector DNA
containing antibiotic-resistance genes (called recombinant DNA or rDNA). The
recombinant strains are then selected using either a direct selection technique or the
replica plating technique.
Velvet covered disk
All colonies from master plate transferred
Press the initially sterile plate
on master plate and
duplicate the
colonies
Master plate:
(supplemented
medium)
Replica plate:
(minimal medium)
Incubation period
Master plate
Replica plate
Missing on
Replicate plate
(nutritional mutant)
Present on
complete medium
(nutritionally normal)
FIGURE 14.2
Duplicate plating method for detecting nutritional mutants.






























































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search