Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(d)
OH
HO
RO
OR
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
HO
RO
O
O
O
OR
OH
HO
4
H CO
O
R = H, or CH CO
COOH
-D-xylose-1
[
→
4-
β
-D-xylose
(2 or 3
←
acetyl)
-1
]
7
→
→
4-
β
-D-xylose-1
→
4-
β
-D-xylose-1
→
4-
β
2
1
4-methoxyl-
α
-glucuronic acid
Stereochemical structure of a common hardwood hemicellulose: glucuronoxylan. For every 10
xylose units, about 7 of them were partially acetylated on the C-2 or C-3 positions.
(e)
OH
O
OH
HO
O
OH
O
HO
OH
OH
O
O
HO
O
O
O
HO
OH
O
O
COOH
HO
α
4-
β
-D-xylose-1
→
4-
β
-D-xylose1
→
3-
-D-rhamnose-1
→
2-
α
-D-galacturonic acid-1
→
4-
β
-D-xylose
→
Structure of the birch xylan reducing end.
α
-D-rhamnose and
α
-D-galacturonic acid residues are
present just prior to the reducing end
β
-D-xylose unit.
(f)
CH OH
CH OH
CH OH
HO
HO
O
O
O
OH
O
O
O
O
O
O
OH
OH
HO
HO
HO
OH
O
OH
O
CH OH
CH OH
x
Hardwood hemicelluloses: glucomannan,
x
≥
0. For every
-D-glucose unit, there are one to two
-
β
β
D mannose units depending on the wood species.
FIGURE 2.25
(Continued).
phosphate from phytate and hydrolyzes the complexes formed by phytate and metal
ions or other cations, rendering them more soluble, ultimately improving and facilitating
their intestinal absorption. Ascorbic Acid (vitamin C) can reduce phytic acid effects on
iron.
OOP(OH)
2
OH
(HO)
2
POO
HO
Phytase
(HO)
2
POO
OOP(OH)
2
OH
OH
+
6 H
3
PO
4
(HO)
2
POO
HO
OOP(OH)
2
OH
(inositol)
(phytic acid)




















































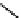


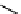







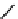













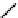





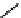









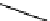



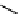





















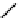
































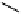


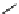








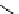

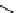
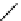










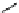

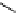



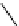







































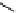





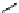
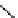
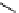




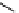




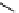




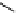







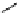

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search