Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
CH
2
OH
CH
2
OH
O
RO
O
OR
RO
O
O
O
O
O
OR
OR
HO
OH
O
RO
O
O
CH
2
OH
OH
HO
O
CH
2
OH
R =
OCCH
3
or H
HO
4-β-D-glucose-1
4-β-D-mannose
(2 or 3
Acetyl)
-1
4-β-D-mannose
(2 or 3
Acetyl)
-1
4-β-D-mannose
(2 or 3
Acetyl)-1
6
1
-D-galactose
α
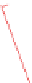
Principle structure of galactoglucomannans. The OH groups in the mannose units were partially
substituted by O-acetyl groups on the C-2 or C-3 positions, i.e. R = CH
3
CO or R = H.
(b)
OH
OH
O
HO
O
HO
O
O
O
O
O
HO
O
O
O
O
O
OH
OH
HO
OH
H
3
CO
HOCH
2
O
OH
COOH
4-β-D-xylose-1
4-β-D-xylose-1
4-β-D-xylose-1
4-β-D-xylose-1
4-β-D-xylose-1
5
3
6
1
1
4-methoxyl-α-D-glucuronic acid
α-L-arabinofuranose
2
Principle structure of arabinoglucuronoxylan. α-L-arabinofuranose units are present among the β-
D-xylose units and 4-methoxyl-α-D-glucouronic acid residues.
(c)
OH
OH
HO
O
O
OH
O
HO
HO
OH
OH
OH
O
O
O
HO
O
OR
O
OH
HO
HO
HO
OH
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
OH
OH
OH
3
Principle structure of arabinogalactan, where R is
β
-D-galactopyranose, or less frequently
α
-L-
arabinofuranose, or
β
-D-glucuronic acid residue.
FIGURE 2.25
Stereochemical structure of common softwood and hardwood hemicelluloses molecules.









































































































































































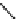













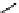
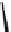





















































































































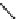

































Search WWH ::

Custom Search