Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CH
2
OH
CH
2
OH
OH
OH
HO
O
O
HO
O
O
O
OH
O
HO
HO
O
OH
OH
O
CH
2
OH
CH
2
OH
FIGURE 2.24
Structure of cellulose. Repeating units are shown between the two dashed lines.
Inulin is a linear polymer of fructofuranose through
b
(2
1) connections, with a terminal
a
-
D
-
glucopyranose, while Levan is a linear homopolymer of
b
-
D
-fructofuranose through
b
(2
/
6)
/
connections. Graminan, however, is a polymer of
b
-
D
-fructofuranose, with both
b
(2
1) and
/
b
(2
6) connections.
/
2.3.2.3.4. CELLULOSE
Cellulose is a long, unbranched chain of
b
-
D
-glucose with an MW between 50,000 and
10
6
Da. Cellulose is the most abundant carbohydrates on earth, which makes about 40%
of the woody (or pant) biomass. The linkage between glucose monomers in cellulose is
a
b
-1,4 glycosidic linkage (
b
-1
/
4-
D
-glucopyranose), as shown in
Fig. 2.24
.
-1,4 glycosidic bond is resistant to enzymatic hydrolysis: only a few microorganisms
can hydrolyze
The
b
-l,4 glycosidic bonds in starch or glycogen
are relatively easy to break by enzymatic or acid hydrolysis. Efficient cellulose hydrolysis
remains one of the most challenging problems in attempts to convert cellulosic wastes into
fuels or chemicals.
b
-1,4 glycosidic bonds in cellulose.
a
2.3.2.3.5. HEMICELLULOSES
Hemicelluloses are a collection of heteropolymers of five- and six-carbon sugars with short-
branched side connections. Common hemicellulose molecules include galactogluco-
mannans, arabinoglucuronoxylan, arabinogalactan, glucuronoxylan, and glucomannan.
The last two are abundant in hardwoods, whereas the first three appear more in softwoods.
Figure 2.25
shows these typical softwood and hardwood hemicellulose molecules. While
cellulose is linear or one-dimensional, most hemicellulose molecules are two-dimensional
polymers as shown in
Fig. 2.25
.
2.3.2.4. Phytic Acid and Inositol
Phytic acid is found within the hulls of nuts, seeds, and grains. In-home food preparation
techniques can reduce the phytic acid in all of these foods. Simply cooking the food will
reduce the phytic acid to some degree by autohydrolysis. More effective methods are soaking
in an acid medium, lactic acid fermentation, and sprouting.
Phytic acid has a strong binding affinity to important minerals such as calcium, magne-
sium, iron, and zinc because of the multiple phosphate groups. When a mineral binds to
phytic acid, it becomes insoluble, precipitates and will be inabsorpable in the intestines.
This process is highly dependent on pH.
Probiotic lactobacilli, and other species of the endogenous digestive microflora as
well, are an important source of the enzyme phytase which catalyzes the release of



















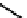






















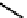


Search WWH ::

Custom Search