Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Q
,
S
0
(1 -
y
s
)
Q
S
e
,
X
e
X
,
S
Waste water
Effluent
(1 +
R
)
Q
V, X, S
Settling tank
or Separator
Air
RQ
S
R
,
X
R
Q
S
R
=
c
Rs
S
X
R
=
c
R
X
(
R + y
s
)
Activated sludge reactor
or Oxidation ponds
y
s
Q, S
R
,
X
R
Excess sludge
FIGURE 12.12
Schematic diagram of a typical wastewater processing unit.
approaches PFR behavior: circular tanks approach CSTR. The concentrated cells from the
settling tank are recycled back to the stirred-tank reactor. Usually, a mixed culture of organ-
isms is utilized in the bioreactor. Some of these organisms may produce polymeric materials
(polysaccharides), which help the organisms to agglomerate. Floc formation is a common
phenomenon encountered in activated sludge processes, which may impose some mass
transfer limitations on the biological oxidation of soluble organics; but good floc formation
is essential for good performance of the system, since large dense floes are required in the
sedimentation step. Cell recycle from the sedimentation unit improves the volumetric rate
of biological oxidation (i.e. high-density culture) and therefore reduces the residence time
or volume of the sludge reactor for a given feed rate. The recycle maintains the integrity of
biocatalysts (microbials) in the process in case of minor upsets or fluctuations. The recycle
ratio needs to be controlled to maximize BOD removal rate.
The selection of aerator and agitators is a critical factor in the design of activated sludge
processes. The aeration requirements vary depending on the strength of the wastewater
and cell concentration. Oxygen requirements for a typical activated sludge process are about
30
e
60 m
3
-O
2
/kg-BOD removed. Various aeration devices with and without mechanical
agitation can be used in activated sludge units. Mechanical surface aerators are widely
used for shallow activated sludge units. Surface aerators consist of partially submerged
impellers attached to motors mounted on fixed structures. Surface aerators spray liquid
and create rapid changes at the air
e
water interface to enhance oxygen transfer. Pure oxygen
may be used for high-strength wastewater treatment. Also, stagewise operation with pure
oxygen has been found to be a very effective method of wastewater treatment. The UNOX
Process, first developed by Union Carbide, is based on this concept. Other forms of aeration
include bubble aerators and fixed turbines.
The activated sludge system faces many uncontrolled disturbances in input parameters,
such as waste flow and composition. Such disturbances can lead to system failure (less
than adequate treatment of the waste stream). One type of disturbance is referred to as
shock
loading
. A shock load indicates the sudden input (pulse) of a high concentration of a toxic
compound. A CSTR design, of course, is less affected by such inputs than a PFR design.
One response to disturbances is sludge
bulking
.A
bulking sludge
has flocs that do not settle
well, and consequently cell mass is not recycled.
Bulking
sludge often results from a change in









































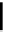






Search WWH ::

Custom Search