Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
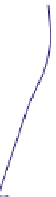
α-Helical coil
Supercoiling of α-helical coils to form
ropes
Fibrous Protein
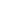
The tertiary structure
of a single-chain
globular protein
The quaternary structure of
a multichain or oligomeric
globular protein
Globular Proteins
FIGURE 2.12
Fibrous and globular proteins.
Although the sequence of amino acids determines a protein's primary structure, the
secondary and tertiary structures are determined by the weak interactions among the
various side groups. The ultimate three-dimensional structure is critical to the biological
activity of the protein. Two major types of protein conformation are (1) fibrous proteins
and (2) globular proteins.
Figure 2.12
depicts examples of fibrous and globular proteins.
Proteins have diverse biological functions, which can be classified into five major
categories:
(1)
Structural proteins: glycoproteins, collagen, keratin.
(2)
Catalytic proteins: enzymes.
(3)
Transport proteins: hemoglobin, serum albumin.
(4)
Regulatory proteins: hormones (insulin, growth hormone).
(5)
Protective proteins: antibodies, thrombin.
Enzymes represent the largest class of proteins. Over 2000 different kinds of enzymes are
known. Enzymes are highly specific in their function and have extraordinary catalytic power.











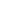

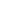


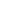
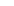

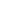

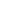



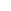

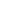


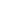

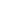
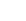



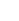

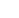

Search WWH ::

Custom Search