Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
available sites in each layer and the excess heat of adsorption decrease each layer by an
equal fixed amount. This assumption leads to
exp
E
max
RT
exp
E
max
nRT
K
1;j
K
nþ1;j
¼
K
i1;j
K
i;j
¼
c
1=n
c ¼
;
¼
Derive the adsorption isotherm expression similar to the way UniLan isotherm is
obtained.
9.2.
When deriving at multilayer adsorption isotherms,
Eqns (9.80) and (9.82)
, we have
assumed steric interactions: desorption can occur only if the adsorbed molecule is not
covered by the layer above it. Rework P9.1 with
n
2 (or three layers), however, follow
the multilayer adsorption derivation with the additional steric interaction implied.
9.3.
The following data were recorded for the adsorption of a gas on a solid:
¼
Equilibrium Pressure, mmHg
Volume Adsorbed cm
3
/g
0
C
25
C
100
C
T[
T[
T[
2
0.12
0.31
5.8
3.5
0.21
0.54
10.3
5
0.31
0.8
14
7
0.48
1.2
21
10
0.8
2.0
32
15
1.7
4.3
56
20
3.1
7.8
91
30
7.7
19
210
40
15
38
380
(a)
Plot the three isotherms on a log
e
log scale.
(b)
The heat of adsorption can be related to the equilibrium pressure at constant level of
adsorption through Clausius
e
Clapeyron equation,
d
lnP
d
T
¼
DH
RT
2
. Determine the
heat of adsorption and plot the heat of adsorption as a function of surface coverage
(or level of adsorption).
(c)
Is the Langmuir adsorption isotherm a good assumption? Why? How about Temkin
isotherm?
(d)
Examine the quality of adsorption isotherm fit with ExLan.
(e)
Examine the quality of adsorption isotherm fit with Multilayer model.
9.4.
The mechanism proposed by Topchieva (K.V. Topchieva, R. Yun-Pun and LV. Smirnova,
Advan. Catalysis,
9, 799, 1957) for ethanol dehydration over Al
2
O
3
,is
(1)








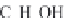















Search WWH ::

Custom Search