Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Sintering:
loss of activity due to a decrease
in active surface per volume of catalyst, nor-
mally the
result of
excessively high
temperatures.
n
A vast effort has been expended over the
years in investigation of these types of deac-
tivation as they are encountered in catalytic
reactions and catalysts of technological
importance. The uninitiated are often
amazed at the fact that many reaction-
system process designs are dictated by the
existence of catalyst deactivation, as are
process operation and optimization strate-
gies. In some cases, the deactivation behavior is so pronounced as to make detailed studies
of intrinsic kinetics of secondary importance.
In the catalytic reaction rate expressions we have seen so far, the number of active centers
is the key factor or activity of the catalyst. When viewed in mathematical terms, catalyst deac-
tivation is reduced to the change of the number of active centers. This is illustrated in
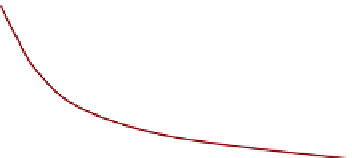
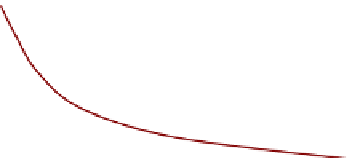
Fig. 9.14
. The loss of active centers can be due to a number of reasons as outlined above.
From this point on, the mechanism of catalyst deactivation can be modeled again via reaction
kinetics. Therefore, the kinetics we have been discussing so far can be applied to catalyst
deactivation as well.
0
0
t
FIGURE 9.14
Variation of number of active centers
with the service time of a catalyst.
9.7. SUMMARY
Reactions occurring on solid surface start with reactants or catalyst from the fluid phase
collide and associate with active centers (or sites) on the surface.
A
þ s
%
A
$s
(9.1a)
or for dissociative adsorption
A
2
þ
2s
%
2
A
$s
(9.10)
which is governed by
E
ad
RT
E
des
RT
r
A
¼ k
A
e
qC
s
C
A
k
0
A
e
q
A
C
s
(9.2a)
or in terms of dissociative adsorption
E
ad
RT
E
des
RT
r
A
2
¼ k
A
2
e
2
C
2
s
C
A
2
k
0
A
2
e
2
A
C
2
q
q
(9.12a)
s
These equations form the bases for analyses of the reactive fluid
e
surface interactions. The
adsorption isotherms are derived from
Eqn (9.2)
and/or
Eqn (9.12)
together with the total







Search WWH ::

Custom Search