Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a) Determine the activation energy for the reaction.
(b)
How long would it take to reach 1.10% acid at 38
F?
(c) If you left yogurt out at room temperature, 77
F, how long would it take to reach
1.10% lactic acid?
7.9.
Table P7.9
shows data on bakers' yeast in a particular medium at 23.4
C and various
oxygen partial pressures were obtained:
p
O
2
, mmHg
0
0.5
1
1.5
2.5
3.5
5
Lm
O
2
, mmHg, no sulfanilamide
0
23.5
33
37.5
42
43
43
Lm
O
2
, mmHg, with 20 g/L
sulfanilamide
0
17.4
25.6
30.8
36.4
39.6
40
(a) Calculate the maximum oxygen uptake rate
and the Monod saturation
constant
K
S
when no sulfanilamide is present. Monod equation is given by
m
O
2
max
m
O
2
¼
m
O
2
max
S
K
S
þ S
where
S
is the concentration of oxygen. In this case, oxygen pressure could be used.
(
b) Determine whether sulfanilamide is a competitive or noncompetitive inhibitor to the
O
2
uptake. For competitive inhibition
m
O
2
¼
m
O
2
max
S
K
S
þ S þ K
I
I
and for noncompetitive inhibition
m
O
2
¼
m
O
2
max
S
ðK
S
þ SÞð1 þ I=K
I
Þ
where
I
is the concentration of the inhibitor.
7.10.
Diene 110 is synthesized in benzene via:
CHO
C(O)OCH
2
[(CH
3
)
2
CHO]
3
Al
2
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
A
B
At 28
C, the concentration of A was measured as given in
Table P7.10
.
t
, h
0
3
6
9
12
C
A
, mol/L
2
1.08
0.74
0.56
0.46
Determine the reaction rate expression.
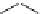




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search