Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Case A).
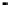
Case B).
y
y
x
x
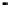
Case C).
Case D).
y
y
x
x
FIGURE 7.6
Schematics illustrating the quality of fits.
case C. In addition, the data are consistently higher the regression line. It becomes obvious
that the regression model missed the hump in data in the middle range.
In regression analysis, we know that the data contain error. However, we shall assume that
the data do not have systematic error. Therefore, we must require the regression line to be lie
in the center of the data
d
bias of the data in relative to the regression line means either the
parameters are not correctly estimated or the model needs to be improved. Whether the
data and regression show any bias, graphic illustrations are the best means to detect. Bias
and/or imprecision is not easy to define and detect mathematically. One must visually assess
the quality of the fit. If there is a bias in the fit, one can improve the regression by adjusting
the initial guess (as there might be more solutions to the nonlinear optimization problem)
and/or improving the regression model.
7.8. BATCH KINETIC DATA INTERPRETATION: DIFFERENTIAL
REGRESSION MODEL
In this section, we shall discuss the parametric estimation for one particular class of regres-
sion model: differential model. This type of problem is commonly encountered in Physical
















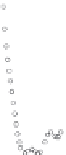
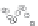

















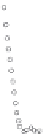


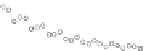






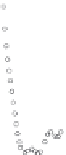
































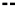















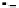





















































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search