Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
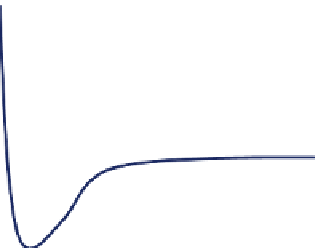
a)
Hard sphere interaction
0
0
Intermolecular distance
b)
0
0
Intermolecular distance
FIGURE 6.1
Mutual potential energy diagrams for model and real systems. (a) Hard-sphere interaction
potential as a function of center-to-center intermolecular distance. (b) Molecular interaction potential energy as
a function of intermolecular distance.
the collision between two hard-sphere molecules as shown in
Fig. 6.2
. Before collision, we
have molecule A, with mass m
A
, diameter
s
A
, and velocity v
A
, and molecule B, with mass
m
B
, diameter
s
B
, and velocity v
B
. If there are no tangential forces acting in the collision, which
we shall assume, the velocities involved in energy transfer during collision are those parallel
to the line of centers, as indicated on the
Fig. 6.2
. From momentum and energy conservation
balances, one obtains the postcollision velocities in terms of the precollision values:
v
0
A
¼
2
m
v
B
v
A
ð
m
B
m
A
Þ
B
(6.4)
m
A
þ
m
B















Search WWH ::

Custom Search