Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Q
e
,
C
e
,
T
e
C
,
T
C
,
T
C
,
T
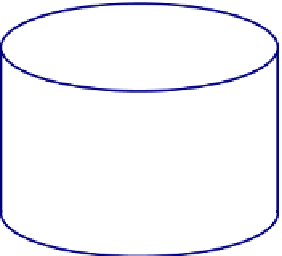
FIGURE 3.10
Schematic diagram of a batch reactor shown.
(1) Batch reactor. An ideal batch reactor has no mass flow into or out of the reactor. Inside the
reactor, the contents are well mixed. The concentrations and temperature, for example,
are identical everywhere inside the reactor at any given instant in time. However, they
can vary with time.
Figure 3.10
shows an illustration of a batch reactor.
(2) Plug flow reactor or in short PFR. A PFR is a completely segregated flow reactor, in which
the contents are completely mixed transversely at any given location on the axial (flow
direction) location. However, along the direction of flow, there is absolutely no mixing.
Therefore, the concentrations and temperature can vary along the axial (flow) direction
but not transversely or on the plane perpendicular to the direction of flow. PFR is an
idealization of a tubular reactor.
Figure 3.11
shows an illustration of a PFR.
(3) Continuous stirred-tank reactor, CSTR, or chemostat. A CSTR has mass flow into and out
of the reactor that is otherwise a batch reactor. Therefore, the contents in a CSTR are well
mixed. The concentrations and temperature are identical anywhere inside the reactor,
which are also the same as those in the effluent. However, the feed stream can have
different values.
Figure 3.12
shows an illustration of a CSTR.
The well mixedness of a CSTR gives rise to unique properties for the reactor operation.
Often, when the term CSTR is used, we refer to the steady state operation of a CSTR. In this
case, the concentrations of any given species in the effluent and the same as those inside the
reactor are constant, also independent of time. For any bioprocesses, the production of prod-
ucts is usually catalyzed by biological cells and/or catalysts. As we will learn later in the topic,
V
V
+d
V
V
= 0
u, C
,
T
Q
e
,
C
e
,
T
e
u, C
,
T
Q
0
,
C
0
,
T
0
u, C
,
T
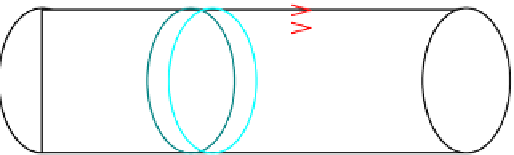
FIGURE 3.11
Schematic diagram of a PFR. It can be thought if as a tubular reactor with the velocity (u),
concentrations (C), and temperature (T) uniform at any given plane along the axial direction.






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search