Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
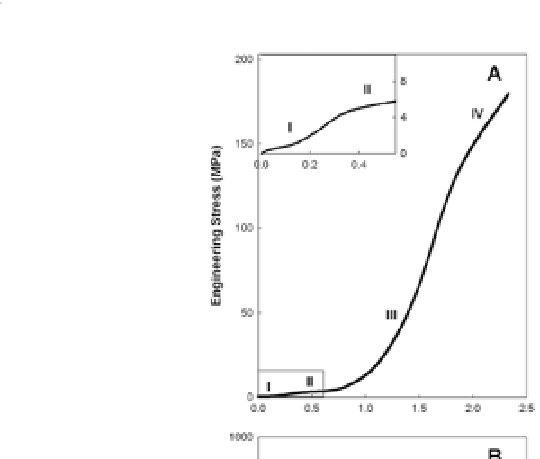
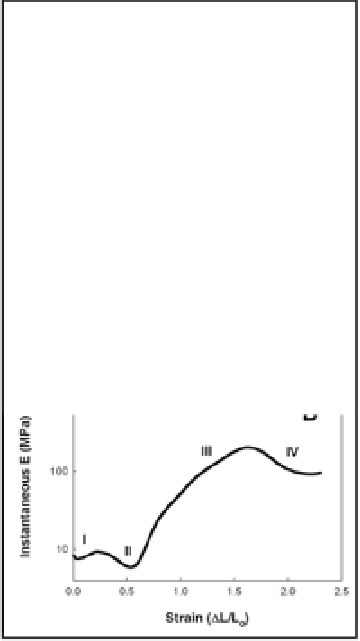
Figure 2.5
Tensile mechanics of slime threads. (a) Stress-strain curve
for a single slime thread measured using a glass rod force
transducer apparatus. (b) A plot of the instantaneous slope
of the curve in (a), which makes is easier to see the different
mechanical regimes denoted by the roman numerals. With
permission from
.
11
Biophysical Journal
This means that the threads can stretch to more than three time
their original length before they break. For individual slime threads,
this corresponds to a breaking length of 34 cm. The extensibility and
stiffness of materials are typically inversely correlated, so it is not
surprising that hydrated slime threads have a fairly low stiffness
of approximately 6 MPa, which is similar to that of rubber-like
biomaterials.
20,21
Comparable to rubber, slime threads are able to
stretch reversibly to considerable strains. Unlike rubber, however,
which behaves elastically at all strains up to its breaking point, slime
threads yield at a strain of approximately 35%. Strains that exceed
the yield strain are not reversible and lead to an increase in the
resting length of the thread after it is unloaded
11
(Fig. 2.6).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search