Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
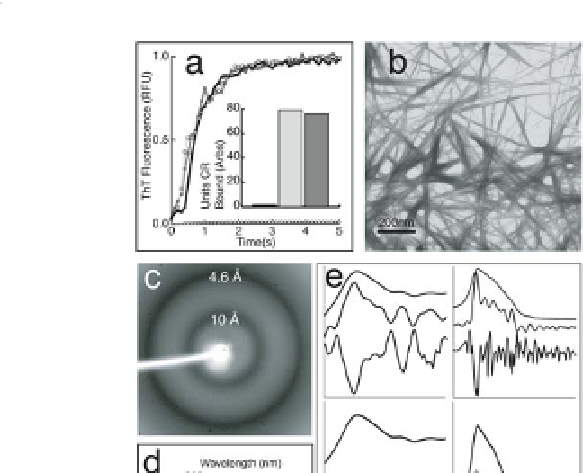
Figure 9.2
Recombinant Mα (rMα) forms amyloid
. (a) rMα fibre
formation at varying pHs: pH 7.4 (black line, triangles), pH 6.0
(dark grey line, circles), and pH 4.85 (light grey line, squares);
control (thioflavin T buffer; black line, white diamonds).
The inset bar graph reflects endpoint Congo red binding of
equimolar amounts of Mα (dark grey), Aβ 1-40 fibres associated
with Alzheimer disease (light grey), and control (Congo red
buffer; black). (b) Transmission electron micrograph of typical
rMα amyloid fibres with an average diameter of 10 nm. (c)
X-ray powder diffraction of lyophilized rMα fibres exhibit a
very strong reflection at 4.6 Å and a strong reflection at 10 Å,
which is expected of an
in vitro
amyloid cross β-sheet structure. (d)
The far-UV CD spectra of soluble Mα aggregates formed at low
concentrations to avoid precipitation support a predominantly
β-sheet structure. Mα aggregates are approximately 11%
α-helix, 32% β-sheet, 23% β-turn, and 33% disordered, based
on curve fitting with a
basis set of 43 soluble proteins. (e)
The attenuated total reflectance FT-IR spectrum of rMα fibres
supports a β-sheet-rich structure.
Peaks in the amide III (top
left, upper curve) and I (top right, upper curve) regions were
identified using Fourier self-deconvolution (top left and right,
middle curve) and
analysis
(top left and right, bottom curve). Reproduced from Fowler
et al
confirmed by second derivative
5
.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search