Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
(iv)
If the relative eccentricity vanishes,
E
= 0, then we arrive at the special Hammer projection of
the sphere
A
1
S
subject to
c
1
=2
,c
2
=1
,c
3
=1
/
2, and
c
4
=1,namely
x
=2
r
(
Λ, Φ
)cos
α
(
Λ, Φ
)
, y
=
r
(
Λ, Φ
)
,
sin
α
(
Λ, Φ
)
,
(H.93)
cos
Φ
sin
Λ/
2
sin
Φ
1
1
cos
α
(
Λ, Φ
)=
cos
2
Φ
cos
2
Λ/
2
,
sin
α
(
Λ, Φ
)=
cos
2
Φ
cos
2
Λ/
2
,
(H.94)
−
−
r
=
A
√
2
1
−
cos
Φ
cos
Λ/
2
,
(H.95)
x
=2
A
1
√
2
1+cos
Φ
cos
Λ/
2
, y
=
A
1
√
2
cos
Φ
sin
Λ/
2
sin
Φ
1+cos
Φ
cos
Λ/
2
.
(H.96)
End of Corollary.
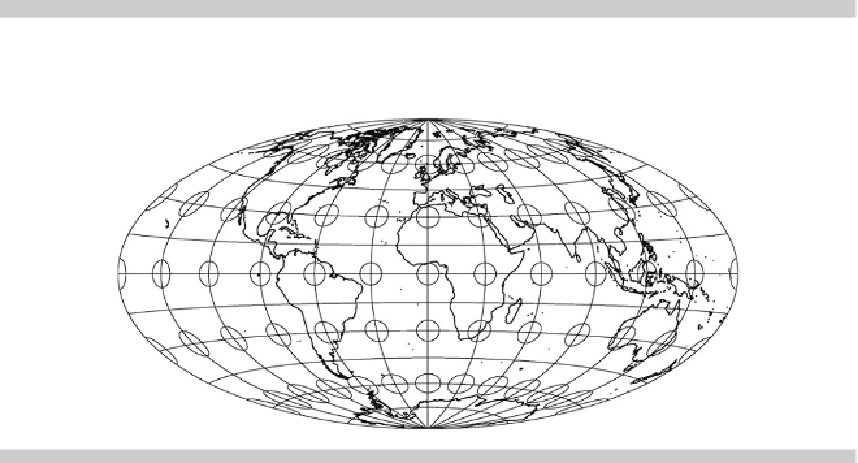
As a visualization for the derived mapping equations for the
ellipsoidal Hammer projection
,at
the beginning of this section, Fig.
H.3
is given including the
Tissot indicatrices
.
Fig. H.3.
The ellipsoidal Hammer projection, squared relative eccentricity
E
2
=0
.
1
H-3 An Integration Formula
Equation (
H.28
) may be written as an integration formula. The following relations (
H.97
)-(
H.100
)
specify this integration formula. If the relative eccentricity approaches
E
= 0, then the radial
coordinate specializes to (
H.101
) according to the L'Hopital Rule (
H.102
)and(
H.103
).
sin
x
1+
p
2
sin
2
x
d
x
=
−
2
cos
x
1+
p
2
sin
2
x −
1
1+
p
2
2
p
p
cos
x
1+
p
2
,
arcsin
(H.97)
subject to











Search WWH ::

Custom Search