Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
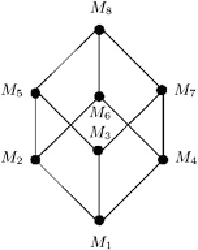
Fig. A.9.
Hasse diagram for power(
A
),
|
A
|
=3,
|
power(
A
)
|
=8
A-2 Law and Order: Fibering
For a set system (which we experienced by power (
A
), for instance)
M
=
{
A
1
,A
2
,...,A
n
}
,
i
=1
A
i
intersection
and
union of the set system. The inverse
operation of the union of a set system, namely the
partioning
or
fibering
of a set system into
specific subsets is given by the following definition.
i
=1
A
i
and
we call
∩
M
=
∩
∪
M
=
∪
Definition A.4 (Fibering).
∈
N
∗
) of subsets
M
1
,...,M
n
is called a
partioning
or a
A set system
M
=
{
M
1
,M
2
,...,M
n
}
(
n
fibering
of
M
if and only if
(i)
M
i
=
∅
for any
i
∈{
1
,
2
,...,n
}
,
(ii)
M
i
∩
M
j
=
∅
for any
i, j
∈{
1
,
2
,..., n
}
,
=
i
=1
M
i
(iii)
M
=
M
1
∪
M
2
∪
...
∪
M
n
=
∪
M
holds. These subsets of
M
, the elements of
M
, are called
fibres
of
M
or of
M
, respectively.
End of Definition.
In other words,
M
1
,...,M
n
are
non-empty subsets
of
M
, their paired
intersection M
i
∩
M
j
is the
empty set
and their ordered
union
is
M
again.
Example A.5 (Fibering).
N
∗
,
M
1
=
Let
M
=
{
1
}
,
M
2
=
P
(set of prime numbers)
and M
3
=
{
x
|
ab
=
x
for any
a
∈
P
and
∈
N
∗
\{
for
b
1
}}
the set of compound numbers. Then
M
=
{M
1
,M
2
,M
3
}
(A.14)
is a
partitioning
or a
fibering
of
M
. For instance,
M
1
=
{
1
},
M
2
=
{
2
,
3
,
5
,
7
,
11
,
13
,
17
,...},
(A.15)
M
3
=
{
4
,
6
,
8
,
9
,
10
,
12
,
14
,...
}




Search WWH ::

Custom Search