Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Box 1.12 (Eckert II, the fourth problem).
(tr[C
l
G
−
l
])
2
=4det[C
l
G
−
l
]
,
Λ
1
=
Λ
2
⇔
(1.88)
det[C
l
G
−
l
]=1
,
(1.89)
(tr[C
l
G
−
l
(
Λ
=0
,Φ
=0)])
2
=
64 + 9
π
2
2
=4det[C
l
G
−
l
]=4
⇒
Λ
1
=
Λ
2
.
(1.90)
24
π
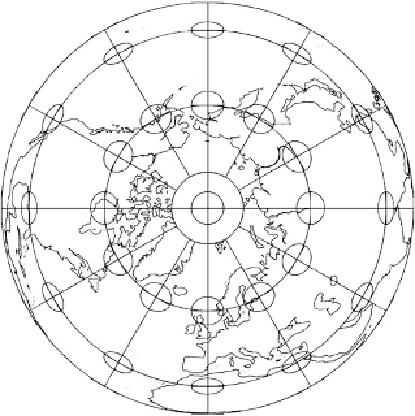
Example 1.6 (Orthogonal projection of points of the sphere onto the equatorial plane through
the origin).
Let us assume that we make an orthogonal projection of points of the northern hemisphere onto
the equatorial plane
2
R
+
.Figures
1.10
and
1.11
illustrate such
an azimuthal projection by means of polar coordinate lines, shorelines, and right Tissot ellipses
of distortion. The mapping equations are given by
x
=
X, y
=
Y, Z >
0
,x
=
R
cos
Φ
cos
Λ, y
=
R
cos
Φ
sin
Λ
.
2
O
P
through the origin
O
of the plane
S
End of Example.
S
2
R
+
onto the tangent plane
P
2
O
at the North Pole,
Fig. 1.10.
Orthogonal projection of points of the sphere
shorelines, right Tissot ellipses of distorsion
We pose two problems. (i) Derive the right Cauchy-Green deformation tensor. (ii) Solve the right
general eigenvalue-eigenvector problem.







Search WWH ::

Custom Search