Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
10-23 Equal Area Mapping (Lambert Projection)
Λ
1
Λ
2
=1
⇒
f
(
Φ
)
R
cos
Φ
0
cos
Φ
=1
⇒
(10.12)
d
f
=
R
cos
Φ
cos
Φ
0
d
Φ
⇒
d
f
=
f
(
Φ
)=
R
sin
Φ
cos
Φ
0
+const
.
As before, the integration constant is determined from the additional constraint that for
Φ
=0the
coordinate
y
should be zero, namely
y
=0
const. = 0. Therefore, the mapping equations are
provided by (
10.13
). The left principal stretches are provided by (
10.14
). Compare with Fig.
10.6
.
⇒
x
y
=
R
Λ
cos
Φ
0
,
(10.13)
sin
Φ
cos
Φ
0
Λ
1
=
cos
Φ
0
cos
Φ
, Λ
2
=
cos
Φ
cos
Φ
0
.
(10.14)
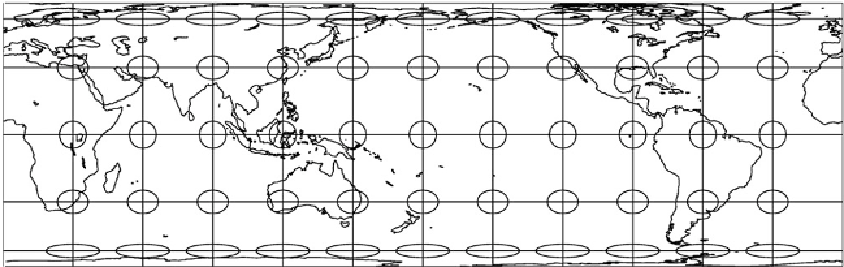
Fig. 10.6.
Mapping the sphere to a cylinder: polar aspect, equal area mapping,
Φ
0
=0
◦
: tangent cylinder
(normal Lambert cylindrical equal area projection)






Search WWH ::

Custom Search