Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
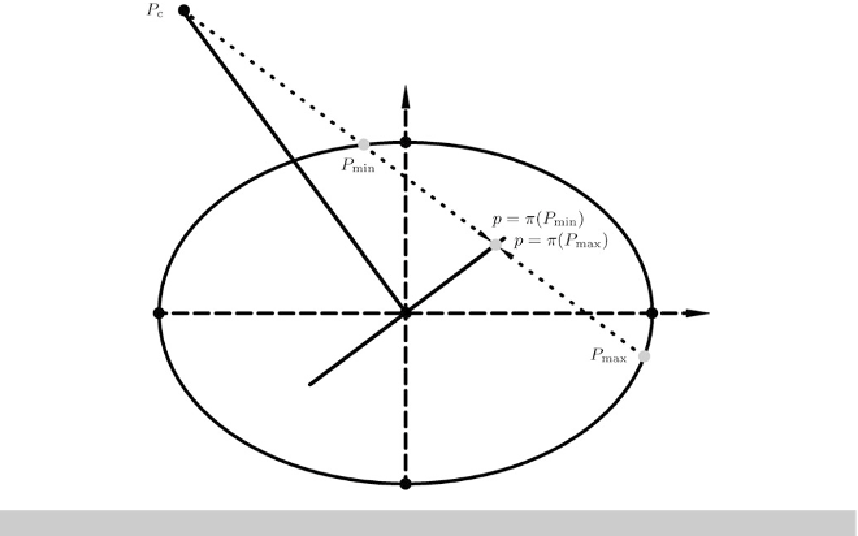
Fig. 8.6.
Perspective mappings of a perspective center
P
c
to the plane which passes the center
O
of the ellipsoid-
E
2
A
1
,A
2
of-revolution
8-31 The First Derivation
The first derivation of the perspective equations is based upon the
fundamental perspective graph
denoted by
P
c
P
0
P
as illustrated by Fig.
8.11
. Here, we take advantage of the basic equations which
are based upon the so-called
normal intersection
in terms of the curve
P
0
P
, which coincides with
the intersection line
E
A
1
,A
2
and
P
P
c
P
0
P
.Notethat
δ
is the angle of the cone in the triangle
P
0
,P
c
,P
at
P
c
, Furthermore, note that the point
P
0
locates the point of minimal distance with
respect to the point
P
c
and the tangent space
T
P
0
E
at the point
P
0
. Moreover, note that
p
=
π
(
P
) denotes the projection point, which is at minimal distance. In addition,
G
3
is the
normal unit vector extending from
P
0
to
P
c
. Here, we take advantage of the radial coordinate
r
,
the first equation, the second equation, and the third equation, namely
A
1
,A
2
r
=
, P
0
=
p
0
(radial coordinate)
,
P
0
−
P
(8.83)
tan
δ
=
h
or
r
=
h
tan
δ
(first equation)
,
(8.84)

Search WWH ::

Custom Search