Database Reference
In-Depth Information
7. In the Save and materialize Aggregation window, check the “Save Aggregation
as” box and input a name. The checkbox to “materialize aggregation” can also
be selected although it is not required (selecting to materialize will update the
cube aggregates immediately before exiting the Wizard) > Click next.
8. A confirmation message that your aggregation was saved will appear > Click
Finish.
The Wizard will close and the new aggregation script is saved and can be referenced in
batch load and aggregation processes.
Another method for optimizing aggregates is to use user-defined views. When using
this method, the user who is doing the defining is the administrator. They define infor-
mation for each dimension. This information will sway how the views are selected dur-
ing the aggregate process. to access this feature, open EAS and right-click on the outline
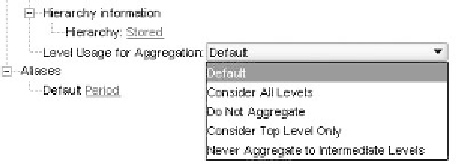
to open it in the outline Editor. right-click on the dimension name and select the
Information tab. near the bottom of the screen, you will see the section for hierarchy
information. Click in the dropdown next to Level usage for Aggregation, as shown in
Figure 5.9, and select the option that best represents how this dimension should be con-
sidered in views. only one can be selected, so go with the 80/20 rule.
For detailed information on each of these choices, and some interesting nuances of
each, see the DBAg.
Query hints are utilized in the final optimization method. remembering that even
the default aggregation provided within Essbase does not aggregate everything (in con-
trast to a BSo default Calc), Query hints are another method to help the system deter-
mine what aggregate views will be most helpful when this cube is queried. There is not
a great deal of documentation, blogging, or research on how well Query hints do or do
not work. After following them through several releases nonetheless, it can be noted that
they continue to change. This speaks to the fact that they must work and that oracle
development sees some degree of value in continuing to provide this feature. Query
hints are created inside of the outline Editor. once an outline is opened, the third tab
is Query hints. using Figure 5.10 as a reference, we can see creating a hint is very simple.
Click on the provided space under the dimension name and select any member from
the level of the dimension that will be queried (only one member is needed). Leaving an
asterisk (*) indicates that any member from that dimension is as likely as any other to
be queried.
In the example shown, one Query hint was added to suggest that monthly data (Jan)
at the summary product level-1 (visual) across any market or account is a likely candi-
date for a view.
Figure 5.9
Level usage for Aggregation options. (From Oracle Essbase Administration Services. With permission.)