Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
water give rise to Gaia, the evolving, self-regulating planetary entity that has maintained
habitable conditions on the surface of our planet over vast stretches of geological time.
This is a radical departure from both the mainstream view which puts the non-bio-
logical processes in control of the Earth, and from the Gaia hypothesis, which had put
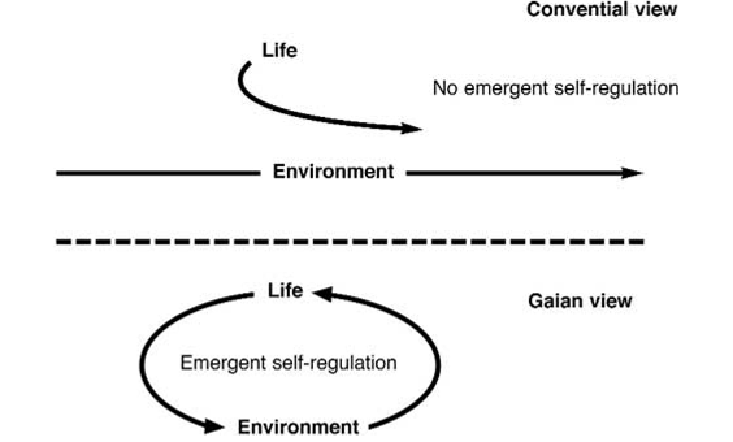
life in charge. Gaia theory suggests that life and the non-living environment are
tightly
coupled
, like partners in a good marriage. This means that what happens to one part-
ner happens to the other, and implies that all the rocks on the Earth's surface, the at-
mosphere and the waters have all been deeply altered by life, and vice versa (
Figure 3
).
The self-regulation arising from this tight coupling is an emergent property that could
not have been predicted from knowledge of biology, geology, physics or chemistry as
separate disciplines. Gaia evolves as an entirety and, like a beehive or a termite colony,
is a superorganism, which for Lovelock is “an ensemble of living and non-living com-
ponents which acts as a single self-regulating system”. Thus the atmosphere is a much
the product of life as is a cat's fur or the bark of a tree.
Figure 3: Non-Gaian and Gaian views of the relationship between life and environment.
Not surprisingly, scientific orthodoxy reacted violently against Lovelock's hypothesis,
declaring that it implied that some kind of mysterious global purpose maintained habit-
able conditions for the entire biosphere over vast periods of time. For mainstream scien-