Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
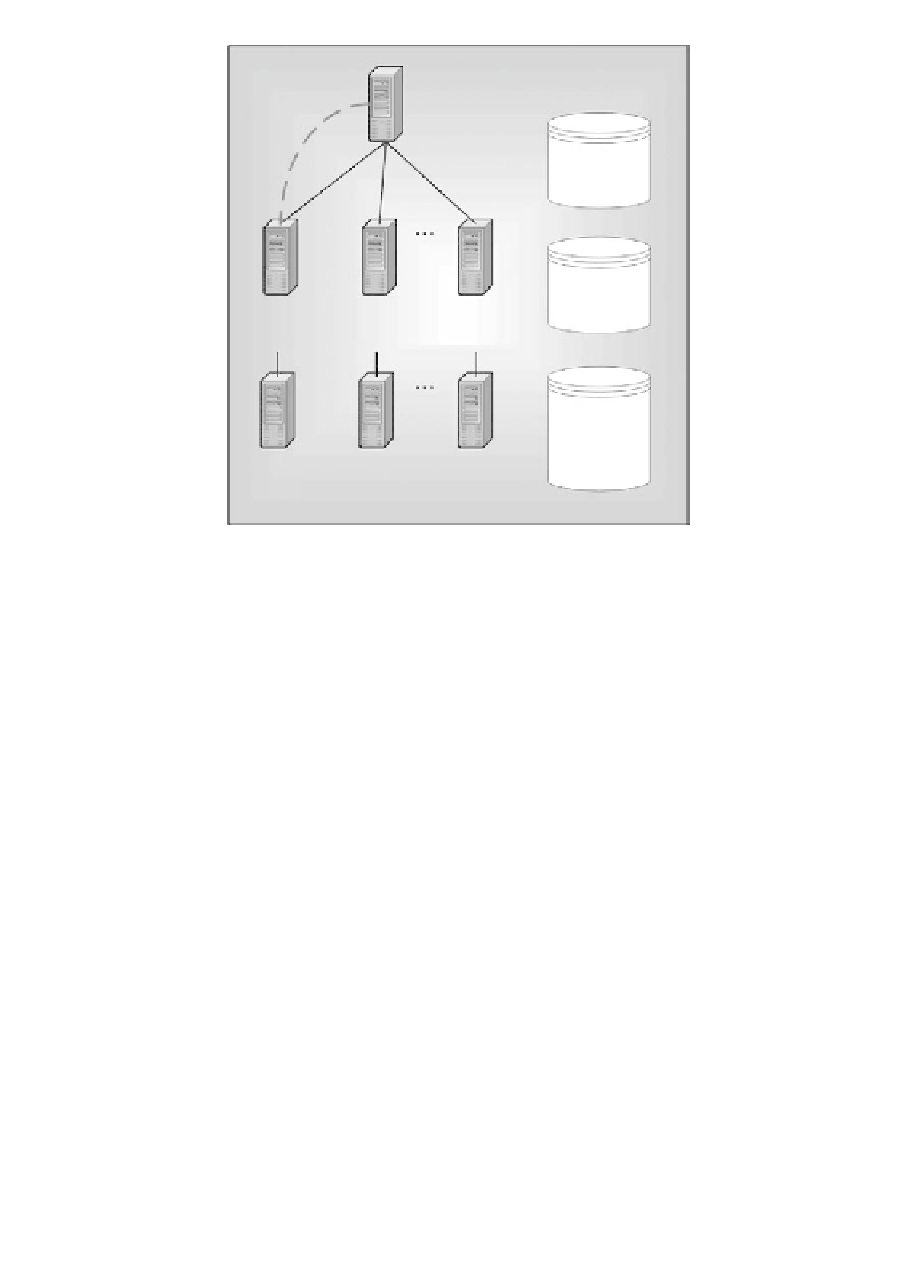
X.509 v3
Certificate
Repository
CA
Root
Certificate
Revocation
List
Region A
CA
Region B
CA
Region X
CA
Backup
Certificate
Repository/
CRL
Site A
RA
Site B
RA
Site X
RA
Figure 9.7
Hierarchical model.
PKI is a difficult concept and it is difficult to implement. The IA
2
Framework
provides a divide-and-conquer approach—the ability to decompose PKI into
smaller, more easily understood chunks. As shown in the overview diagram (Fig-
ure 9.6), there are very clear business motivations behind the PKI technology, clear
business and technical services provided by PKI, and a clear delineation and trace-
ability of mechanics to provide those services to meet requirements.
9.11
oS Security
Operating systems (OSs) come with many security features, including the capabili-
ties for IDs, passwords, and login banners. Moreover, an OS has many configura-
tion options: bootup processes, background services, network share points, local
and remote port activation and access, etc. Securing an OS includes selecting and
configuring the overt security measures, e.g., forcing the use of strong passwords.
Securing an OS also includes finding the not so obvious utilities, background pro-
cesses, and OS configuration parameters that present vulnerabilities. The vulner-
abilities may be in software bugs that require patching, or the vulnerabilities may
be from the manner in which the software is used or in the way the parameters
are set. A secure OS configuration requires removal of unnecessary utilities, turn-
ing off auto-start features on unnecessary background processes, and modifying
parameters that introduce unnecessary operational risk. The IA architecture should