Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
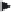
MAS FLOWCHART
2 years
6 months
6-8 months
1 year
Selection of
resistants
(Aprox. 10
genotypes)
Field
test
Green house
Molecular
analysis
2000
SEEDS
Copy In-vitro
Back-up
In-vitro
Embryo
rescue
Selection In-vitro
of resistant
genotypes
Selection of
resistants
(Aprox. 10
genotypes)
Field
test
Shipment
to
partners
Fig. 15.6.
Schematic presentation of MAS workflow followed in introgressing CMD resistance in LA
germplasm and shipment to partners in Africa and Asia. For a color version of this figure, please refer to
the color plate.
the crop's center of diversity in the Neotropics
for other key cassava productions regions of the
world, where CMD is highly endemic (Blair et al.
2007).
CIAT has the largest cassava collection in the
world, with more than 6,000 accessions. CIAT
gene pools have elite cassava lines with very
high yield, high starch content, good dry matter
content, and good plant architecture. The gene
pools for breeding cassava in Africa currently
contain only a fraction of the existing genetic
variation found in Latin America, where the
crop originates. One key area of application of
MAS is in facilitating the introduction of LA
germplasm introgressed with CMD for survival
and adaptation in Africa as an initiative in broad-
ening the germplasm base of cassava in Africa
through access and use of LA germplasm. Cas-
sava is vegetatively propagated and because of
the high susceptibility of LA germplasm, heav-
ily infected LA genotypes are easily and read-
ily wiped out by the second season, as a result
of the build-up of the virus load on the veg-
etative planting materials by the second year.
CMD affects plant vigor and flowering, making
it difficult to utilize unadapted introduced LA
germplasm in crosses with African germplasm.
For this reason, previous attempts to introduce
LA germplasm for evaluation and release as
cultivars in Africa through collaborative a part-
nership between IITA and CIAT in the 1990s
was not very successful. No LA genotypes were
selected for on-farm testing from the IITA breed-
ing scheme (Figure 15.1) because of their high
susceptibility to the disease.
Under a collaborative project between CIAT
and African NARS, elite CIAT lines devel-
oped for CMD resistance with the aid of
markers have been developed and shipped to
Africa. The use of
CMD2
and MAS has rapidly
changed the setback experienced in the 1990s,
leading to the successful introduction of LA
germplasm with broad genetic variation for tra-
ditional breeding traits (yield and other agro-
nomic traits) for the African continent. Follow-
ing the same procedure as described earlier, more
than 1,400 genotypes from F
1
and BC
2
pop-
ulations having CMD parent lines and CIAT


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search