Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
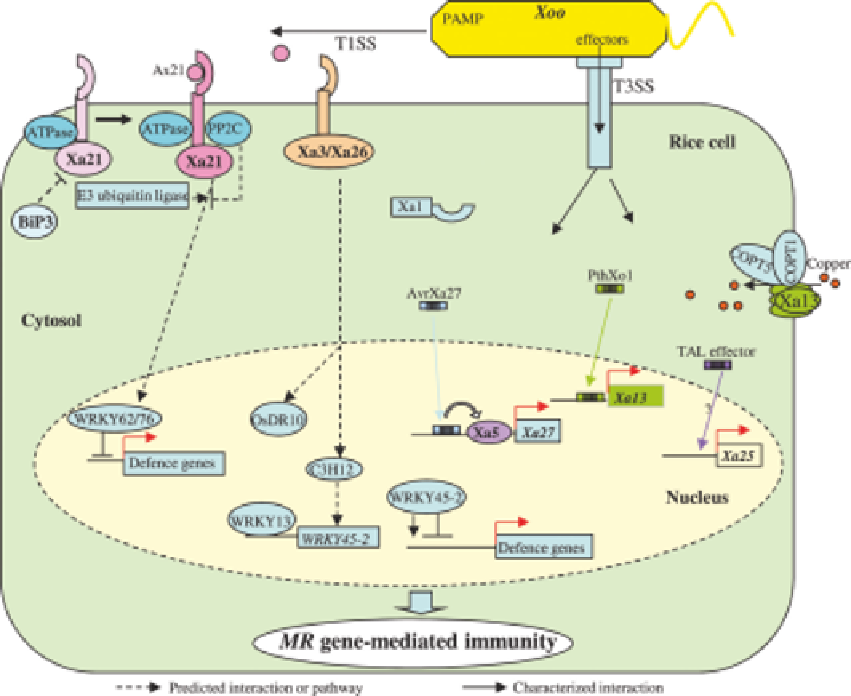
Fig. 2.2.
Molecular mechanisms of characterized major disease resistance gene-mediated resistance to
Xoo
. For a color
version of this figure, please refer to the color plate.
genome of wild rice
Oryza minuta
(BBCC
genome), encode proteins with high sequence
similarity to the Xa3/Xa26 protein and can medi-
ate a similar spectrum of resistance against
Xoo
(Li et al. 2012). The speciation of the AA and CC
genomes is approximately 7.5 million years ago.
These characteristics suggest that the
Xa3/Xa26
locus may confer a durable resistance.
Xa3/Xa26
-mediated resistance is influenced
by the genetic background and the developmen-
tal stage of a plant. This gene confers higher
level of resistance in a
japonica
background than
in an
indica
background, and rice plants carry-
ing
Xa3/Xa26
gene have full resistance to some
Xoo
strains at both seedling and adult stages,
but have full resistance to other
Xoo
strains at
adult stage (Yang et al. 2003; Sun et al. 2004;
Cao et al. 2007a). Further study has demon-
strated that the expression level of
Xa3/Xa26
gene is associated with genetic background- and
development-controlled resistance (Cao et al.
2007a; Zhao et al. 2009).
Xa3/Xa26
-mediated
resistance is dose dependent: as the expression of
Xa3/Xa26
gene increases, the plant's resistance
increases. A
japonica
background facilitates the
expression of
Xa3/Xa26
gene compared with
an
indica
background. In addition, the expres-
sion of
Xa3/Xa26
gene gradually increases with
development and reaches the highest level at the
maximum tillering to booting (panicle develop-
ment) stages. Rice plants constitutively overex-
pressing
Xa3/Xa26
have a high level and broad
Search WWH ::

Custom Search