Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Inkjet head
(liquid adhesive delivery)
Roller
V
Y
Powder bed
V
Z
V
Z
Powder supply platform
Fabrication platform
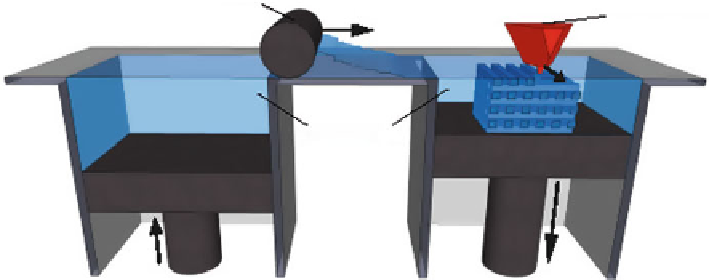
Fig. 9.7
Scheme of a typical 3DP™ set-up. A roller spreads a thin layer of polymer powder over
the previously formed layer, and is subsequently solidified by the spatially controlled delivery of a
liquid binder
workflow can be described in three sequential steps: (1) the powder supply sys-
tem platform is lifted and the fabrication platform is lowered one layer, (2) the
roller spreads the polymer powder into a thin layer (excess powder falls in an
overflow vat) and (3) an inkjet print head prints a liquid binder that bonds the
adjacent powder particles together. The binder can dissolve or swell the powder
particles, causing bonding via the inter-diffusion of polymer chains or via
infiltration of the binder into the powder [
220
]. Cycling steps 1-3 fabricate a 3D
object. A key requirement for 3D printing is the availability of biocompatible
powder-binder systems [
16
]. The powder utilized can be a pure powder or sur-
face-coated powder, depending on the application of the scaffold. It is possible
to use a single, one-component powder, or a mixture of different powders
blended together [
17
]. After the finished construct is retrieved, any unbound
powder is removed, resulting in a complex three-dimensional part. Basic require-
ments that the binder system must satisfy: (1) the binder solution must have a
high binder content while still having a low viscosity so that it is capable of
being deposited by the print head, (2) minimal conductivity may be required for
continuous jet printing heads and (3) the binder must dry or cure rapidly so that
the next layer of particles can be spread [
217
] .
3D Printing has four steps that can limit the rate of the process: the application of
the powder layers, the printing of the binder, the infiltration of the binder into the
powder and the drying of the binder [
217
]. An important advantage of powder-based
systems is the production of rougher surfaces which may enhance cell adhesion [
16
] .
Zcorp developed a 3D printer (Z402) that uses natural polymers as well as
plaster of Paris in combination with a water-based ink [
220,
221
] . This opens
perspectives towards hydrogel manufacturing. A recent detailed review on 3DP™
concerning all process development steps, such as powder-binder selection and
interaction, is given by Utela et al. [
222
] .
Search WWH ::

Custom Search