Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
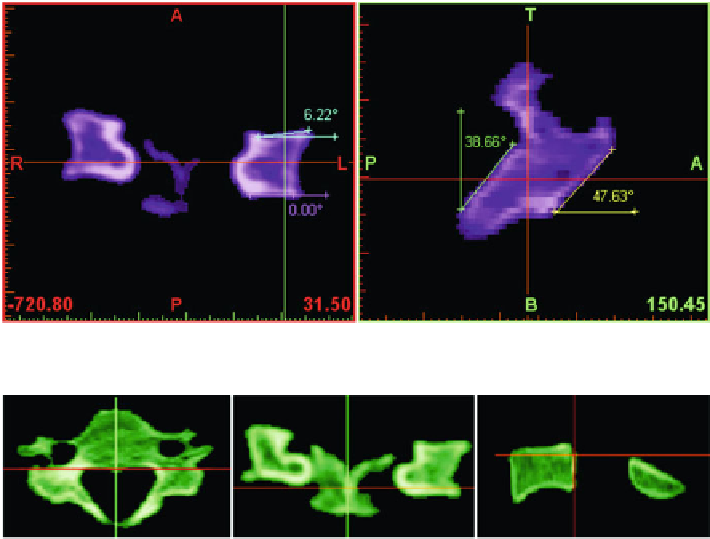
Fig. 7.2
Angles of the facet joints in frontal and lateral planes
Fig. 7.3
Overall color mask applied on slices
These kinds of images are composed exclusively of shades of neutral gray, varying
from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest one [
2,
24
] . In bone
tissue imaging, the dark gray represents the low-density bone tissue and the range
from light gray to white corresponds to the cortical bone tissue.
The image quality was evaluated from both background and areas of interest
point of views. A desirable background is in dark gray tone or black without inten-
sity variations, noise, or artifacts. In this case, the lack of disturbing elements leads
to a high-quality background. The areas of interest have good defined contours
toward the background.
The main purpose of the image processing was to convert the discrete 2D images
into a 3D volume. In order to make this possible all images were imported into
Mimics
image-processing software. The volume conversion protocol uses several
steps of masking the areas of interest. The main characteristic of one mask is the
thresholding interval, which is the simplest method of image segmentation [
24,
38
] .
Using this function, individual pixels in a grayscale image are marked as “object”
pixels if their value is greater than the set threshold value. Typically, an object pixel
has a value of “1” while a background pixel has a value of “0.”
Taking into account that the purpose was to create a multi-solid 3D model
(a model composed of the inner body and outer shell), two different masks were
necessary to be applied. The green mask represents the first mask which was applied
over the entire area of the scanned vertebra, like in Fig.
7.3
.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search