Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
matched to the blue channel of the CCD. The mitochondria were labeled with Mitotracker
Deep Red (Invitrogen), which was excited by the 632.8 nm laser and had an emission peak
at 670 nm, which closely matched the red channel of the CCD. Since fluorophore emission
is not a single wavelength but rather a broad spectrum, there was some concern that the
nuclear stain could be partially visible in the green color channel, which was used for QPM.
However, since QPM employs off-axis holography, any fluorescence crosstalk that is
concentrated in the low-spatial frequencies is filtered and removed, and therefore does not
significantly affect the phase measurements. The three color channels from each frame were
then processed individually to produce fluorescence maps with molecular specificity and a
quantitative phase image to visualize the overall cellular morphology.
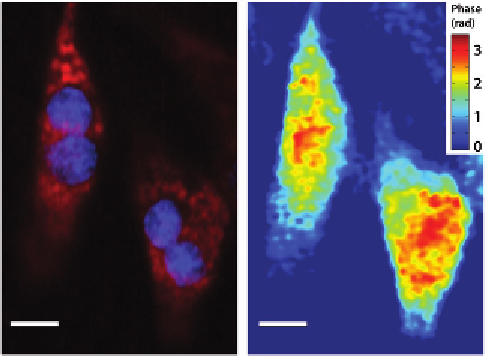
Figure 14.9A
shows
the mitochondrial distribution (red) and nuclear positions (blue) of cardiomyocytes in a
single frame of the sequence, and
Figure 14.9B
shows the quantitative phase map.
There are some unique considerations that arise from the use of an RGB color camera to
multiplex-independent imaging modalities. The mosaic color filter effectively reduces the
number of pixels and therefore the spatial resolution of each independent color channel. To
compensate for this loss, the optical system must be designed to further magnify the object,
which in turn reduces the field of view. The trade-off between resolution and field of view
can be adjusted based on the application and may be alleviated by using a higher pixel
count sensor. A further consideration for separating fluorescence and quantitative phase
information is that commercial digital cameras often perform on-chip image demosaicing
that mixes data from all color channels before outputting the processed image to the user
(A)
(B)
10
μ
m
10
μ
m
Figure 14.9
Rat ventricular cardiomyocytes with (A) fluorescently labeled mitochondria (red) and nuclei (blue),
and (B) quantitative phase delays. Source: Adapted from Ref.
[24]
.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search