Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 13.8
SD-OCM system for measuring OPD of RBCs. Source: Taken with permission from Ref.
[22]
Copyright of SPIE.
The system is illustrated in
Figure 13.8
. The blood sample was placed in a closed
chamber such that the reflection from the upper surface of the chamber is used as the
reference beam and the light passing through the media and the RBC is reflected from the
bottom surface and is used as the sample beam. A compact digital camera arm was added
to the SD-OCM system. The camera displays the light source beam and the sample
bright-field image simultaneously and allows the correct positioning of the light source
beam over the sample.
To demonstrate the system ability to measure live-cell fluctuations, glutaraldehyde-treated
RBCs at various concentration levels were used. Glutaraldehyde causes cross-linking of
proteins and destroys the lipid membrane, leading to an altered structure and thus affecting the
RBC membrane elasticity characteristics. A comparison between the SDPM and a wide-field
digital interferometry (WFDI) system (holographic phase microscopy) is shown in
Figure 13.9
.
By inducing low-membrane fluctuations, it was demonstrated that the system is more
sensitive than commonly used quantitative phase measurement systems, such as ones that
are based on WFDI.
13.4.8 Detection of Gold Nanoparticles
Gold nanoparticles are used as contrast agents to image disease states by targeting to
biochemical makers unique to specific diseases, such as surface membrane proteins in
cancer cells. This in vivo approach currently is being developed as a diagnostic tool and

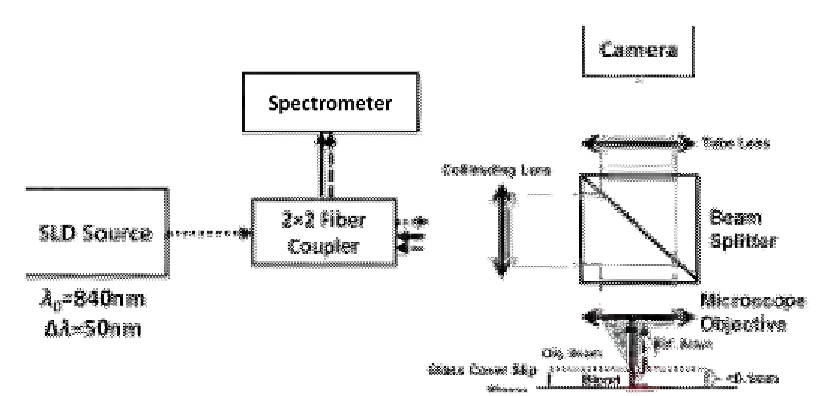
Search WWH ::

Custom Search