Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
microscopy is that, to derive quantitative information, one must know the amount of image
shear. Generally, however, microscope manufacturers do not make that information
available. As a result, one must measure this parameter. Munster et al.
[22]
determined the
lateral shift by measuring the distance between the center of the bright spot and the center
of the dark spot in an image of a submicroscopic transparent latex sphere with bias set at
π
/2. Mehta and Sheppard
[23]
measured shear by studying intensity distribution in the back
focal plane of the microscope objective lens. M¨ ller et al.
[24]
used a combination of
fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering to determine shear.
Duncan et al.
[25]
described a measurement setup with a standard optical wedge.
The technique described later for determining shear distance is simpler, faster, and more
accurate than just mentioned. We measure a shear angle and then compute the shear
amount by employing
formula (2.1)
, as it is explained in the end of this section.
In order to find the shear angle of a DIC prism, we do not need to know how the passing
beam is transformed inside the prism. A DIC prism splits an incident monochromatic plane
wave into two orthogonally polarized plane waves with wavefronts of slightly different
direction.
Figure 2.2
illustrates splitting the incident linearly polarized beam into two
separate output beams with shear angle
. Here, the shear plane is parallel to the
X
-axis. As
one can see in
Figure 2.2
, the shear angle
ε
ε
(in radians) is equal to the derivative of the
optical path difference (bias)
Γ
with respect to the coordinate
x
:
d
d
x
ε
5
(2.4)
Γ
δ
The optical path difference
is connected with retardance
, written in degrees, and
wavelength
λ
in the simple way:
δ
360
λ
Γ
5
(2.5)
Input
wavefront
Output
wavefronts
E
y
E
x
,
E
y
ε
x
E
x
d
Γ
y
z
DIC prism
Figure 2.2
Splitting the incident beam with two orthogonal polarizations E
x
and E
y
by DIC prism into two
separate output beams with shear angle
ε
.


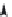




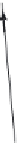


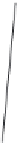
























Search WWH ::

Custom Search