Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
0.25
r
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536
m
2
0
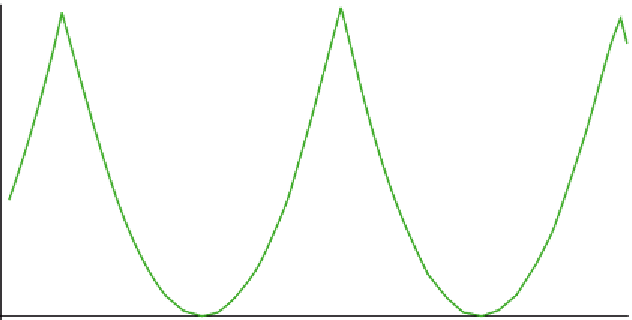
Figure 7.15
Linear regression phase unwrapping: r(m
2
)—the square of difference between m
1
and the nearest
integer. In this example, r(m
2
) has its minimum at m
2
5
11.
set the limit on
m
2
higher. Even if the measurements are very noisy, but the object is only a
few wavelengths high, the maximum number of
m
2
can be set low (much lower than 16 in
the example given earlier), providing a tradeoff between the amount of noise the method
can tolerate and the overall height range.
Consider a slanted surface with the total height of 7.5
m. Simulated phase images of this
surface using two wavelengths (532 and 633 nm) of that structure are shown in
Figure 7.16A and B
. Predictably, each single wavelength phase map shows multiple
discontinuities. By using
Eq. (7.13)
, the algorithm correctly guesses the value of
m
2
(
Figure 7.16C)
, and the unwrapped profile is then easily reconstructed by
Eq. (7.4)
, yielding
the final phase map free of discontinuities (
Figure 7.16D)
. Note that in this case, the overall
height of the objects is more than double the synthetic wavelength
μ
Λ
5
3.3
μ
m.
12
But the real strength of this method lies in the fact that for each point (
x
,
y
), the algorithm
does not rely on the surrounding pixels and so even more topologically complicated images
can be unwrapped just as well. Consider the case where the object is a cell-like semi-sphere,
which has a relatively steep sloped surface on the side. Here, both phase images (
Figure 7.17A
and B)
were also corrupted by random (up to 2 rad) phase noise. Additionally, the object is
placed to the edge of the image frame, so for each phase jump, a single wavelength software
algorithm has only a few pixels to work with. As evident from
Figure 7.17C
, it fails to unwrap
the phase correctly, while the linear regression method produces a correct profile, without
amplifying the noise. It is worth noting that the phase noise level here is much higher than
what previous dual-wavelength algorithm can tolerate
[10]
.

















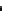












Search WWH ::

Custom Search