Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
λ
(A)
λ
λ
λ
λ
/2
0
(B)
-
λ
/2
λ
/2
Δ
z
(C)
0
-
λ
/2
(D)
λ
/2
(E)
-
λ
/2
λ
/2
Δ
z
(F)
-
λ
/2
(G)
2
Δ
z
(H)
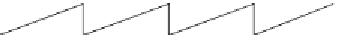
Figure 7.7
Phase unwrapping by varying the reconstruction distance (see text for details).
different phase periods (
Figure 7.7D)
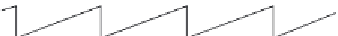
. The distance at which the hologram is digitally
reconstructed can be changed by the small amount
Δz
. By doing so, we effectively move
the object by
Δz
. Then, the phase difference between the object and the reference waves
will also change by a constant and the discontinuities in the phase image will appear at the
different places (
Figure 7.7E)
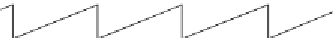
. Then, we choose the part of (E) that is between 0 and
Δz
(
Figure 7.7F)
, shift it up by
Δz
, add the result to map (D), and discard the areas that are not
adjacent (
Figure 7.7G)
. These steps can be repeated (moving up and then down to unwrap
one new area during each repetition), while keeping track of where the new pixels are
added, until the entire phase image is reconstructed “layer by layer” (
Figure 7.7H)
. The
algorithm stops when it finds no new pixels to add to the already unwrapped part of the
image. The size of an individual step cannot be too large to include areas with a
discontinuity. The smaller step size produces the correct solution, but it is more






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search