Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
differential quotient in the
x-
direction of the data in
Figure 6.3D
. DHM DIC is comparable
to Nomarski differential interference phase contrast
[56]
with the advantage of an
adaptable sensitivity due to a variable digital shear
[57]
.
The measurement principle for self-interference DHM as in
Figure 6.2
is illustrated by white
light images and by the evaluation of digital holograms that were obtained from three living
human pancreatic tumor cells (PaTu 8988 T; for details, see Ref.
[29]
and references therein)
by using a 40
3
microscope lens (NA
5
0.6). For both white light imaging and hologram
recording, the specimens were sharply focused onto the CCD sensor.
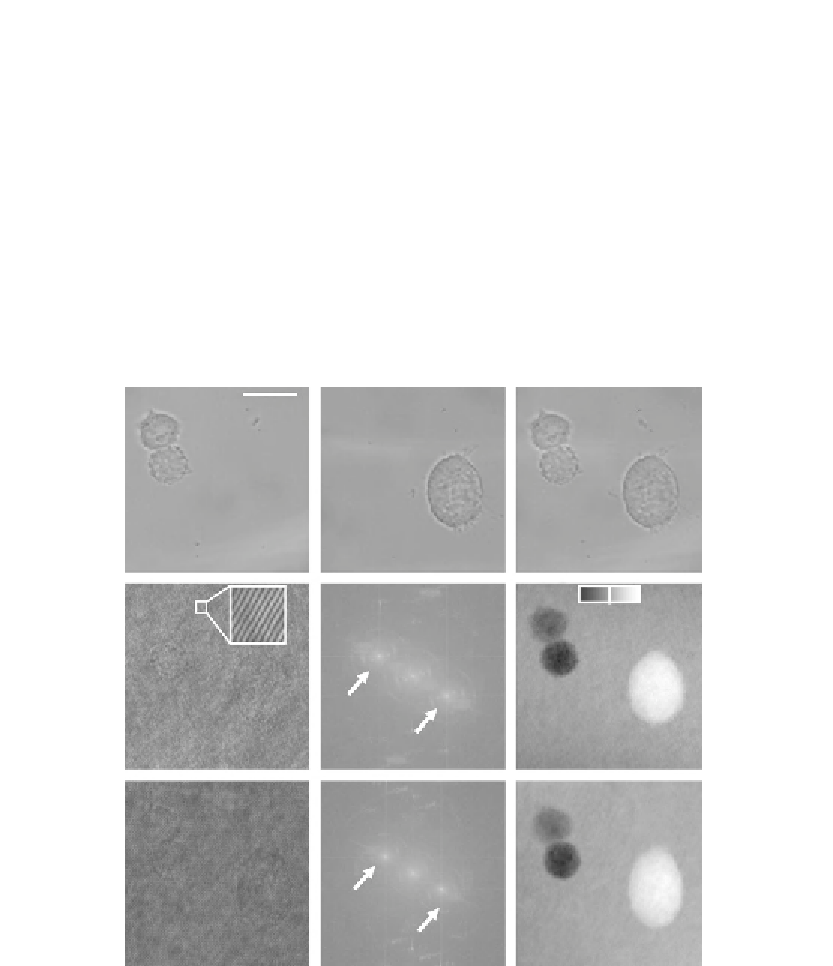
Figure 6.4A
C
shows
white light images of the cells obtained from mirror M1 (optical path of mirror M2 blocked),
from mirror M2 (optical path of mirror M1 blocked), and the superimposed image obtained
by using both mirrors, M1 and M2. For hologram recording, the white light illumination was
replaced by the highly coherent light of a frequency-doubled Nd:YAG laser (
λ
5
532 nm,
20
μ
m
(A)
(B)
(C)
-7.4 rad
+7.4 rad
0
(D)
(E)
(F)
(G)
(H)
(I)
Figure 6.4
Evaluation of self-interference off-axis holograms. (A) White light image (
Figure 6.2
)ofPaTu8988T
cells from mirror M1 (M2 blocked); (B) white light image (
Figure 6.2
) from mirror M2 (M1 blocked);
(C) white light image from M1
M2; (D), (G) digital off-axis holograms with enlarged spatial carrier
fringe pattern; (E), (H): 2D spatial frequency spectra of (D) and (G); (F), (I) quantitative phase
images numerically reconstructed from (D) and (G) (coded to 256 gray levels)
[36]
.
1
Search WWH ::

Custom Search