Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(RP), and is accompanied with the enhancement of postsynaptic GABA response mediated by
ionotropic GABA
A
receptors. Induction of RP depends on the postsynaptic CaMKII activity
and structural alteration of GABA
A
receptor-associated protein (GABARAP), which binds to
both GABA
A
receptor γ2 subunit and tubulin, the component of microtubule [74,75]. A
unique property of RP is that its induction depends on the heterosynaptic excitatory inputs.
Thus, RP induction does not depend on the activity of synapse undergoing potentiation.
However, when GABA is released at an inhibitory synapse during postsynaptic
depolarization, RP induction is suppressed at the synapse [76]. This suppression enables the
synapse-specific regulation of RP. RP suppression is mediated by activation of the
postsynaptic metabotropic GABA
B
receptors, which inhibits CaMKII through a signaling
cascade involving G
i/o
, adenylyl cyclase, cAMP, protein kinase A, dopamine- and cAMP-
regulated phosphoprotein of 32kDa (DARPP-32) and PP1 [77]. RP is also suppressed by
integrin, a cell adhesion molecule, through activation of c-Src [78]. RP induction is occluded
in a δ2 knockout mouse through the enhanced climbing fiber activity
in vivo
[79]. LTD is also
reported at the synapse between a basket/stellate cell and a Purkinje cell [80].
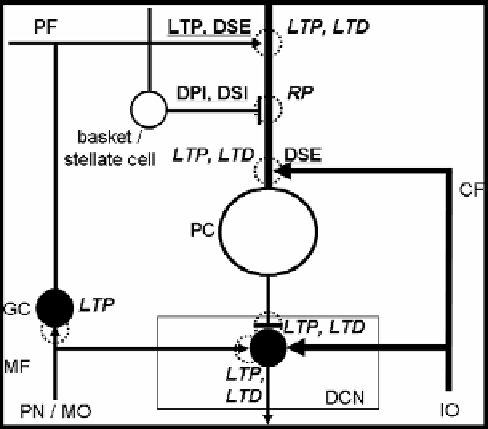
Figure 3. Various forms of synaptic plasticity in the cerebellum. Underlined words indicate the synaptic
plasticity expressed presynaptically and
ITALIC
words indicate that expressed postsynaptically. Filled
circles and arrows show somata and axons of excitatory neurons. Open circles and lines ended with bars
indicate somata and axons of inhibitory neurons. Dpi: depolarization-induced potentiation of inhibition,
dse: depolarization-induced suppression of excitation, dsi: depolarization-induced suppression of
inhibition, ltd: long-term depression, ltp: long-term potentiation, rp: rebound potentiation. Cf: climbing
fiber, dcn: deep cerebellar nuclei, gc: granule cell, io: inferior olivary nuclei, mf: mossy fiber, mo:
medulla oblongata, pc: purkinje cell, pf: parallel fiber, pn: pontine nuclei.
LTP and LTD have also been reported at climbing fiber - Purkinje cell synapses [81,82].
In P14-26 rats, LTD is induced by repetitive stimulation of a climbing fiber, depending on the
increase in postsynaptic intracellular Ca
2+
and on the PKC activity [81]. Multiple climbing
fibers innervate a Purkinje cell in a neonatal rat. The number of innervating climbing fibers
decreases during development, resulting in the strong innervation by one climbing fiber by
P20. In P6-9 rats, a Purkinje cell is innervated by one strong climbing fiber and several weak