Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
localized at the postsynaptic membrane of parallel fiber - Purkinje cell synapses, although it
does not seem to work as an ion-conducting channel [13,14].
Since a climbing fiber forms numerous synapses on a Purkinje cell, a single action
potential can induce a strong postsynaptic depolarization through activation of AMPA
receptor, leading to large Ca
2+
influx through voltage-gated Ca
2+
channel, which is
abundantly expressed in dendrites of Purkinje cells [15] (Figure 2).
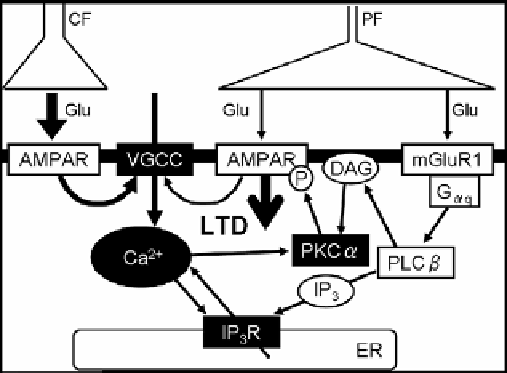
Figure 2. The main molecular signaling pathways involved in induction of the cerebellar LTD. The
candidates of coincidence detectors are shown in white characters. AMPAR: AMPA receptor, CF:
climbing fiber, DAG: diacylglycerol, ER: endoplasmic reticulum, G
αq
: Gq protein α subunit, Glu:
glutamate, IP
3
R: IP
3
receptor, mGluR1, metabotropic type I glutamate receptor, PF: parallel fiber,
PKCα: protein kinase Cα, PLCβ: phospholipase Cβ, VGCC: voltage-gated Ca
2+
channel.
The increase in the intracellular Ca
2+
concentration is necessary for the induction of LTD.
Glutamate released from a parallel fiber activates AMPA receptor and mGluR1. mGluR1
activates phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ) through G
αq.
PLCβ produces inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate
(IP
3
) and diacylglycerol (DAG) from phosphatidylinositol biphosphate (PIP
2
) in the plasma
membrane (Figure 2). IP
3
is released to the cytoplasm, where it binds to IP
3
receptors on the
membrane of endoplasmic reticulum and induces Ca
2+
release from the endoplasmic
reticulum to the cytoplasm. Thus, both the Ca
2+
influx through voltage-gated Ca
2+
channel
and the Ca
2+
release from the intracellular store cooperatively increase the intracellular Ca
2+
concentration. DAG produced by mGluR1/PLCβ pathway activates protein kinase C (PKC)
together with Ca
2+
[16]. PKC phosphorylates the PSD-95/DlgA/zo-1 (PDZ) domain binding
motif in the C-terminus of GluR2 subunit of AMPA receptor [17]. LTD induction depends on
the activity of PKCα but not of PKCγ, another subtype of PKC abundantly expressed in
Purkinje cells [18]. This specificity is ascribed to the PDZ-binding motif found in PKCα, but
not in PKCγ. In the basal condition, AMPA receptors are accumulated in the postsynaptic
membrane and bind to glutamate receptor interacting protein (GRIP) [19]. After
phosphorylation of GluR2 by PKCα, AMPA receptor is released from GRIP and binds to
protein interacting with C-kinase-1 (PICK1) [17]. The binding to PICK1 is thought to lead to
endocytosis of the receptor. Thus, AMPA receptor on the postsynaptic membrane is reduced