Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
4.A
4.B
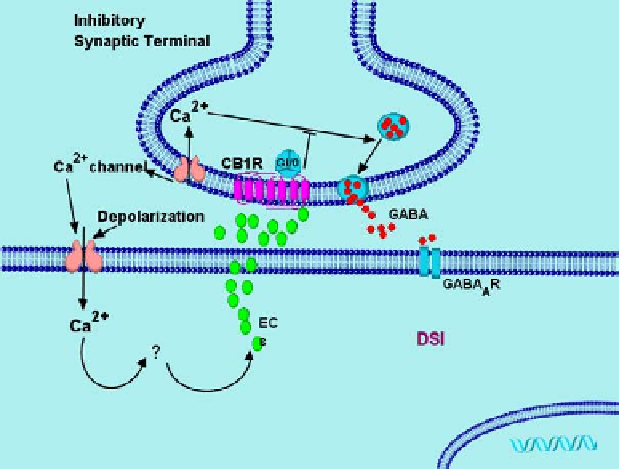
Figure 4. Schematic diagram to illustrate the mechanism of depolarization-induced suppression of
inhibition (DSI) and depolarization-induced suppression of excitation (DSE). Depolarization of a
postsynaptic neuron leads to Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Elevation of
intracellular Ca2+ concentration triggers biosynthesis of endocannabinoids. Endocannabinoids are then
released from postsynaptic neurons, activate CB1 receptors at presynaptic neuron, and suppress GABA
(DSI) (A) or glutamate (DSE) (B) release by inhibiting Ca2+ channels [95, 100, 177]. GluR, Glutamate
receptors.