Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
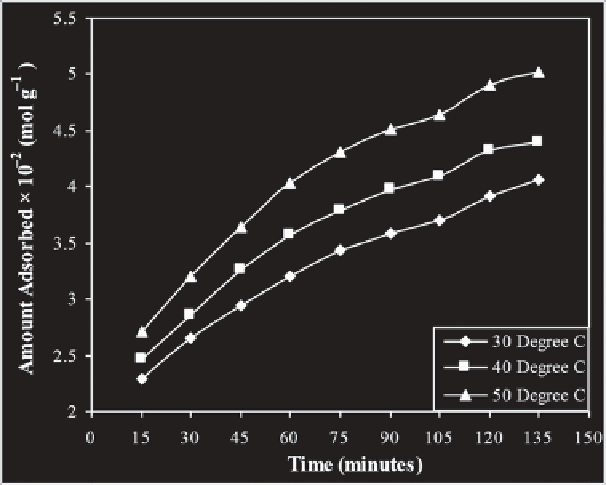
Figure 11.7
Effect of contact time for the uptake of Amaranth (9 × 10
-5
M, pH 2.0) by
Hen Feathers at different temperatures.
for the designing of any sorption system. The information gathered under
various isothermal conditions during the course of investigations is uti-
lized to evaluate useful thermodynamic parameters, which suggest the fea-
sibility, favorability and spontaneity of the ongoing adsorption process in
each dye-adsorbent system. Moreover, the chemical or physical character
of the adsorption has also been investigated in the present studies for both
the dyes.
11.5.1
Adsorption and Adsorption Isotherm Models
Adsorption is a surface phenomenon which involves the accumulation
or concentration of substances at a surface or interface. This process can
occur at an interface of any two phases, such as liquid-liquid, gas-liquid,
gas-solid or liquid-solid. Therefore, adsorption is a process in which the
molecules or atoms of one phase interpenetrate nearly uniformly among
those of another phase to form a solution with this phase. As such the
solute remaining in the solution is in dynamic equilibrium with that at the
surface of the adsorbed phase.
Adsorption is related to the phenomenon of surface energy. In a bulk
material, all the bonding requirements, whether ionic, covalent or metallic,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search