Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
globally high rate of consumption and undesired impacts on aquatic life
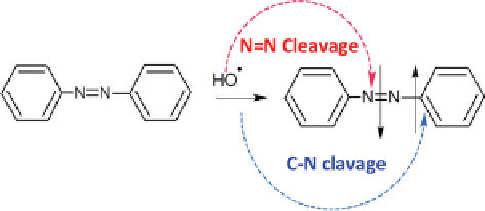
[5,17,22,24,25,34-41]. The mechanism of azo dye destruction by sonolysis
is based on HO addition to the chromophore, i.e., the N=N or C-N bonds
of the molecule, as depicted in Figure 7.1. Generally, it has been shown
by density functional theory (DFT) calculations or other means that the
priority of HO attack is the azo bond [23,42], while the role of electron
transfer reactions is also of significance [43].
The high water solubility and polar nature of azo dyes hinder their diffu-
sion to the gaseous cavitation bubbles, where very extreme conditions are
available for high-energy chemistry. As such, azo dyes are not expected to
undergo thermal decomposition under ultrasonic irradiation. This hypoth-
esis was validated by Singla
et al.
[3], who carried out sonoluminescence
(SL) analysis in the present of an azo dye and reported that no SL quench-
ing relative to that of water occurred, thus neither the dye nor its degrada-
tion byproducts were thermally decomposed at the cavitational bubble or
the interfacial area [3]. On the other hand, other researchers demonstrated
that depending on the applied frequency and the experimental conditions,
some of the dye molecules may diffuse away from the bulk solution to reach
the bubble-liquid interface, where they are exposed to considerably larger
concentrations of HO than in the bulk liquid [17,44]. As such, the chemi-
cal reactions and the potential reaction sites of an azo dye exposed to ultra-
sonic irradiation are as presented in Equations 7.12-7.13 and Figure 7.2,
respectively.
Dye + HO
[Dye-OH adduct]*
Oxidized dye + CO
2
+ H
2
O (7.12)
Dye + )))
R + Dissociated dye fragments + C
2
H
4
(7.13)
where [Dye-OH adduct]* is an excited intermediate product resulting
from the addition of an HO onto -C-N- or -N=N- bonds, and R is an
organic radical dissociated from the dye.
Figure 7.1
Hydroxyl radical addition to N=N or C-N bonds of the ring [42].








Search WWH ::

Custom Search