Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
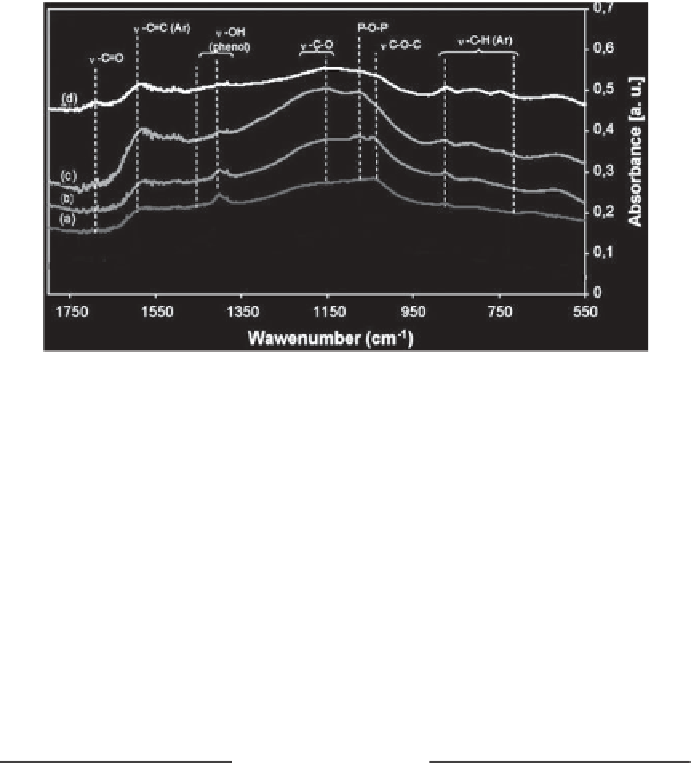
Figure 5.28
FTIR spectra of activated carbons: CGAC30 (a), CGAC60 (b), CGAC120 (c),
and CGAC180 (d) [117].
Table 5.24
Langmuir adsorption capacity of methylene blue onto the activated
carbons and the surface areas of materials covered by methylene blue molecules
[117].
Activated
Carbon
Adsorption
Capacity
(
mg.g
-1
)
Surface area covered
by methylene blue,
S
MB
(%)
Methylene blue
coverage ratio,
S
MB
/S
BET
(%)
Mesopore
coverage
ratio, S
ext
/
S
BET
(%)
CGAC30
*
96.1
264
51
39
CGAC60
*
129.9
357
58
61
CGAC120
*
163.9
452
61
79
CGAC180
*
181.8
501
54
93
*
CGAC(n) represents the activated carbon with an impregnation ratio of “n” wt%.
characterization showed that most of the carbons were bonded together as
aromatic rings for the activated carbon, while these aromatic rings were
not observed in the raw material. Furthermore, the appearance of C-N
stretching vibrations for the dye-loaded adsorbent confirmed the presence
of the dye molecules on the surface of the adsorbent. The FTIR spectra of
the original material, activated carbon and the dye-loaded adsorbent have
been illustrated in Figure 5.29. The maximum adsorption capacity of the
activated carbon for the malachite green was found to be 244
g.g
-1
, which
was comparable with many commercial and laboratory-prepared activated
carbons. The effect of the addition of salt in the adsorption capacity of the
prepared activated carbon is shown in Figure 5.30. Since the adsorbent and












































Search WWH ::

Custom Search