Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
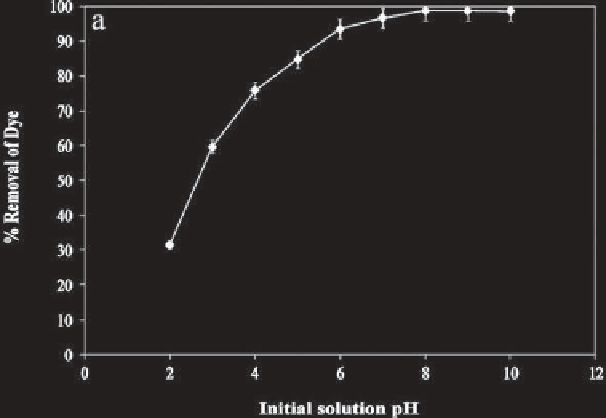
Figure 5.1
Effect of pH on adsorption of CV using treated rice husk [46].
to an increase in the dye removal amount. Also the effect of adsorbent dose
was considered as a prominent parameter that strongly affects the adsorp-
tion process. It was shown that the removal percent increased, but the
maximum dye uptake decreased by increasing the adsorbent loading. They
attributed this phenomenon to the increasing number of adsorption sites
as the adsorbent loading increases to a certain extent. However, further
increase in the adsorbent dose results in the aggregation of the adsorbent
particles, which in turn would lead to a decrease in the surface area of the
adsorbent and a reduction in the removal percent. Furthermore, Figure 5.2
illustrates that the removal percentage of the dye molecules was decreased
by raising the temperature. It was related to the weakening of the bonds
between the surface functional groups of the adsorbent and the dye mol-
ecules. The adsorption mechanism of crystal violet (CV) dye molecules
was perceived to consist of several steps; dissociation of the dye molecules
into CV
+
and Cl
-
, dissociation of surface hydroxyl groups of the adsorbent,
migration of dye molecules from the bulk of the solution to the adsorbent
surface, diffusion of the dye molecules from the boundary layer to the sur-
face of the adsorbent, hydrogen bonding between the nitrogen atoms of
the dye molecule and hydroxyl moieties of the adsorbent surface sites via
dye-hydrogen ion exchange process. The possible adsorption mechanism
of CV onto rice husk has been illustrated in Figure 5.3.
Many authors have used various acid treatment methods in order to pre-
pare activated carbon from rice husk for wastewater treatment purposes.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search