Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
series. This model retains spatial network information while reducing the temporal
replication needed in other models, thus resulting in a much more efficient model for
several computational techniques for routing problems. In this chapter, we discuss
spatio-temporal networks as represented by time-aggregated graphs at a conceptual,
logical, and physical level. This chapter also focuses on shortest path algorithms
for spatio-temporal networks. We develop the topics via case studies using TAGs in
context of Lagrangian shortest-path queries and evacuation route planning.
6.6
Snapshot Model
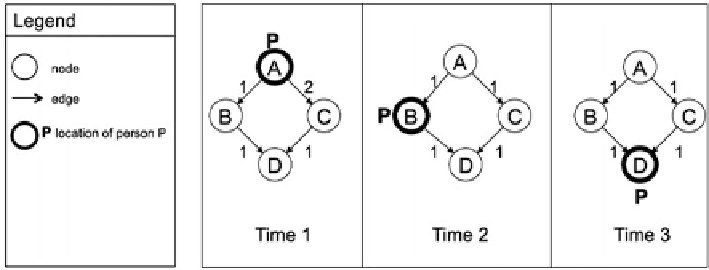
A network that changes over time can be modeled as a series of networks, each
associated to a time stamp. Figure
6.4
shows a snapshot representation of the
information presented before as a space-time trajectory in Fig.
6.2
a. As we can
see in Fig.
6.4
, each time instant is represented as a full model of the network.
This representation type is beneficial when trying to compare differences between
different states of the complete network. Instantaneous locations of person P
are shown by bold nodes (and a P symbol) in each snapshot. However, in this
approach, a copy of the network is required for every time step, making it
prohibitively expensive to represent long time series and to use it for computational
modeling.
6.7
Time-Expanded Graphs
To highlight some of these problems with traditional spatio-temporal network
representations we will use a quick example. Operations Research uses a model
called the time expanded network to represent temporal changes in networks
Fig. 6.4
Snapshot model illustrating three time steps
Search WWH ::

Custom Search