Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
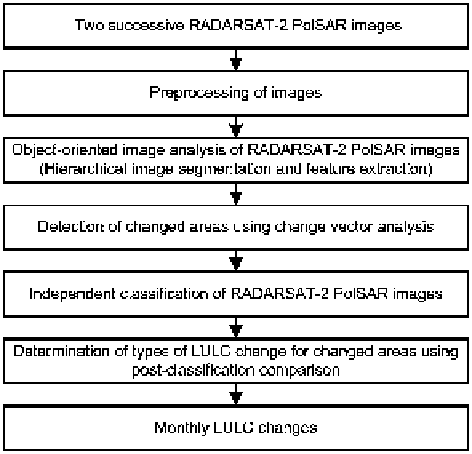
Fig. 19.2
Methodology of
extracting monthly LULC
changes using two successive
RADARSAT-2 PolSAR
images
For example, images acquired on March 21 and April 14 were used to extract LULC
changes between March 21 and April 14, and then images acquired on April 14
and May 08 were used to extract LULC changes between April 14 and May 08.
The methodology of detecting monthly LULC changes using two successive images
based on our previous study (Qi and Yeh
2013
) is shown in Fig.
19.2
.
19.3.1
Preprocessing of RADARSAT-2 PolSAR Images
Image preprocessing, which is critical to change detection, included radiometric
correction, speckle filtering, and image registration. Radiometric calibration for the
RADARSAT-2 images was performed using PolSARPro_v4.1.5 software (López-
Martínez et al.
2005
) and applying the sigma look-up table provided in the product.
After radiometric correction, the pixel values of the images could be directly related
to the radar backscatter of the scene. This is necessary for the comparison of PolSAR
images acquired from the same sensor but at different times. A J.S. Lee Sigma
filter with a window size of 7
7 was applied on the images to reduce speckles.
Compared with other filters, this one effectively retains subtle details and preserves
the shape of small land parcels while reducing the speckle effect (Lee et al.
2009
).
The advantage of this filter will benefit the accurate delineation of tiny land parcels
in object-oriented image analysis. Image registration was based on the geometric
rectification of the RADARSAT-2 images. The PCI Geomatica software was used
to implement the geometric rectification of the images. The RADARSAT-2 image
package provides a total of 180 tie points evenly distributed across the entire image.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search