Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Tabl e 7. 1
Congestion index used by the Beijing Transportation Research Center
Index
[0,2)
[2,4)
[4,6)
[6,8)
[8,10]
Transportation
status
No congestion
Very little
congestion
Slight
congestion
Congestion
Heavy
congestion
Factor for additional
travel time
0
[0.3,0.5)
[0.5,0.8)
[0.8,1.0)
>1.0
researchers have calculated the space-time prism in a (dynamic) transportation
network environment. For example, Miller (
1991
) was the first to develop a network-
based algorithm for computing a space-time prism. Kwan and Hong (
1998
)also
implemented this approach in a transportation network. Wu and Miller (
2001
)
proposed a more realistic space-time prism by taking congestion into account. Based
on the 3D polygon representation of the space-time prisms proposed by Kuijpers
andOthman(
2009
) and Kuijpers et al. (
2010
), Fang et al. (
2011
) proposed a
time-varying network-based prism to identify available activity opportunities for
scheduling joint participation. This chapter formulates a dynamic network-based
space-time prism.
A dynamic transportation network is denoted as
G
(
t
)
Df
V
,
E
,
S
(
t
)
g
,where
V
is a
set of nodes,
V
Df
v
i
D
(
x
i
,
y
i
)
j
0
i
n
g
,
n
is the number of nodes in the network,
E
is a set of edges,
E
Df
e
i
D
(
v
i
,
v
j
)
j
0
i
m
,0
j
m
,
i
¤
j
g
,
m
is the number of
edges in the network,
S
(
t
) is a collection of transport indices on all edges at time
t
,
S
(
t
)
Df
s
(
e
i
,
t
)
j
0
i
m
g
,and
s
(
e
i
,
t
) is a congestion index of edge
e
i
at time
t
.
For example, Table
7.1
lists observed values of the congestion index used here and
as defined by the Beijing Transportation Research Center (Xu et al.
2008
). The
congestion index is calculated according to the combination of travel speed derived
from moving car data, road status, and traffic flow on the corresponding link. A
detailed approach to calculating the congestion index can be found on the Web site
(
http://www.bjtrc.org.cn
)
of the Beijing Transportation Research Center. The ratio
of additional travel time on edge
e
i
means that travelers need more time to pass
through this link. For example, say that it normally takes 10 min for a traveler to
pass through
e
i
. When the congestion index of
e
i
is 3, the evaluated time that a
traveler will need to pass through
e
i
is 10
(1
C
0.4)
D
14 min.
Fang et al. (
2011
) defined a time-varying network-based prism (TVNBP)
between origin
O
and destination
D
within a dynamic transportation network
G
(
t
)
as follows:
f
e
Œ
t
s
;t
e
i
;
v
..x; y/ ; t /
TVNBP
.O;D;T/
D
X
e
i
2
E
(7.1)
f
e
Œ
t
s
;t
e
i
;
v
..x; y/ ; t /
Z
l
e
Z
t
0
max
t
0
max
t
e
;
l
s
;l
e
2
e
i
l
t
0
.x;y/
dldt
;t
s
t
0
min
D
t
min
l
s
(7.2)









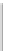





Search WWH ::

Custom Search