Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
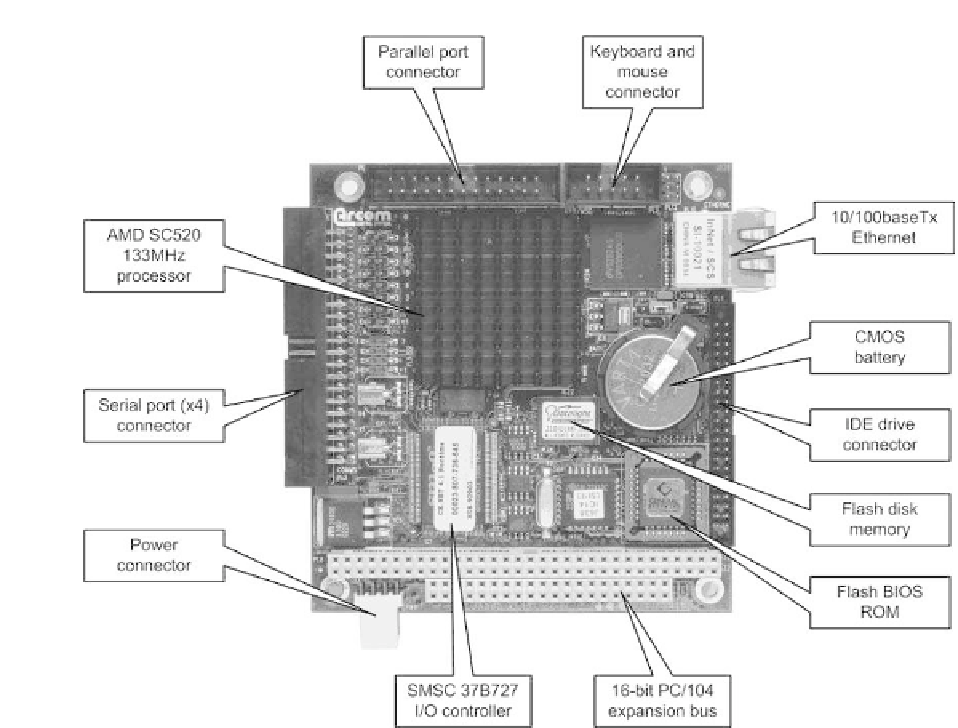
Figure 1.18
Layout of an embedded PC controller
identified on the system board but are also described in the system board manual.
Furthermore, because memory bank configurations can vary from system to
system, it is important to refer to manufacturers' data before attempting to fit
memory modules. Some PCs require
all
the sockets in one bank to be filled
with the same capacity module, some computers require the first bank to house
the highest capacity modules, and others require the banks to be filled in a
particular order!
Most of today's PCs use 168-pin DIMMs, which support 64-bit data paths.
Earlier 72-pin SIMMs supported 32-bit data paths, and were originally used
with 32-bit CPUs. It is important to note that, when 32-bit SIMMs were used
with 64-bit processors, they had to be installed in pairs, with each pair of
modules making up one memory bank.
Data integrity
With early PCs, data integrity checking was based on the use of a simple parity
check of each byte of data. The
parity bit
(stored separately) is used to detect
errors in the other 8 bits. Parity checking may be either
odd
or
even
. In the